【机器学习】用逻辑回归(Logistics Regression)进行分类
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是一种广泛用于二分类问题的统计学习方法。尽管名字中包含“回归”一词,但逻辑回归实际上是一种分类算法,用于估计一个样本属于某个类别的概率。假设函数(Hypothesis Function): 逻辑回归使用sigmoid函数(也称为logistic函数)作为假设函数。模型参数学习(Model Parameter Learning): 通过最大似然估计(
·
算法介绍
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是一种广泛用于二分类问题的统计学习方法。尽管名字中包含“回归”一词,但逻辑回归实际上是一种分类算法,用于估计一个样本属于某个类别的概率。
以下是逻辑回归算法的基本原理:
-
假设函数(Hypothesis Function): 逻辑回归使用sigmoid函数(也称为logistic函数)作为假设函数。
-
模型参数学习(Model Parameter Learning): 通过最大似然估计(Maximum Likelihood Estimation)来学习模型的参数。最大似然估计的目标是最大化观测到的数据的似然概率。对于逻辑回归,可以通过最小化负的对数似然来实现。
-
梯度下降(Gradient Descent): 通过梯度下降等优化算法最小化损失函数。
-
决策边界(Decision Boundary): 通过学习到的参数,可以得到一个决策边界,用于将输入空间分为两个类别。
逻辑回归广泛应用于各种领域,尤其是在二分类问题中,如垃圾邮件分类、疾病诊断等。虽然逻辑回归是一个简单的模型,但它在许多实际问题中表现良好。
数据选用:
fashion_mnist

代码实现
# 导入必要库
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.datasets import fashion_mnist
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,mean_squared_error
(X_train,y_train),(X_test,y_test) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
# 服装类型
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
# 数据预处理 将数据转换成二维
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0],28*28)
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0],28*28)
y_train = y_train
y_test = y_test.astype("int")
# 模型构建
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
result = model.predict(X_test)
# 将预测结果/原始数据转换成字符串
result_obj = [class_names[x] for x in result]
y_test_obj = [class_names[x] for x in y_test]
# 以表格形式对数据进行展示
data_obj = pd.DataFrame({"Actual":result_obj,"Prediction":y_test_obj})
data = pd.DataFrame({"Actual":y_test,"Prediction":result})
# 选取前 100 个数据进行绘制
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
plt.plot(data[:100],marker=".")
plt.show()
# 计算准确值和均方差
print(accuracy_score(result,y_test))
print(mean_squared_error(result,y_test))
"""
accuracy_score : 0.8412
mean_squared_error : 1.9939
"""结果
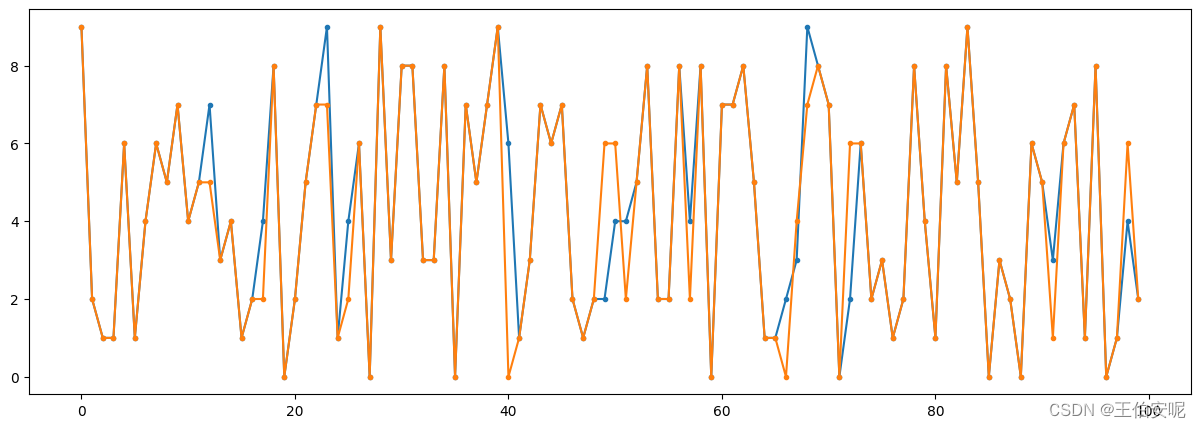
student-mat:G3为期末成绩
数据引用:
代码实现
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# sep=";" 以;分割数据
data = pd.read_csv("student-mat.csv",sep=";")
# 创建一个新列 满足条件值为1否则为0
data["Degree"] = np.where(data["G3"].astype(int) >= 13, "1", "0")
# 选用5个变量作为X
X = data[["studytime","absences","G1","G2","G3"]].astype(int)
y = data['Degree'].values[:,np.newaxis].astype(int)
# 分割数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1)
# 模型创建
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
result = model.predict(X_test)
# 对模型进行评分
score = accuracy_score(result, y_test)
print(score)
# 1 数据简单 拟合较好
print(model.coef_)
# [[-0.02347521 0.05153924 0.19581741 0.82197572 3.49628117]]
# 影响因素 值越大 影响越大
index = ["Bad","Good"]
result_obj = [index[x] for x in result]
y_test_obj = [index[x] for x in y_test.reshape(-1)]
obj_data = pd.DataFrame({"Prediction":result_obj,"Actual":y_test_obj})
print(obj_data)
"""
Prediction Actual
0 Good Good
1 Bad Bad
2 Bad Bad
3 Bad Bad
4 Bad Bad
"""更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容

 https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kYY1UyLh-MoASh6KWg_uJA?pwd=1111
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kYY1UyLh-MoASh6KWg_uJA?pwd=1111





所有评论(0)