swin transformer 核心代码记录
目前更新部分包括swin的基本setting,基本模块,相对位置坐标理解和部分代码展示。swin 包含了四种setting,依次是tiny,small, base 和 large。可以类比resnet。Swin-b 主体部分网络结构BasicLayer结构展示BasicLayer((blocks): ModuleList((0): SwinTransformerBlock((norm1): Lay
目前更新部分包括swin的基本setting,基本模块,相对位置坐标理解和部分代码展示。
基本setting
swin 包含了四种setting,依次是tiny,small, base 和 large。可以类比resnet。
整个流程图
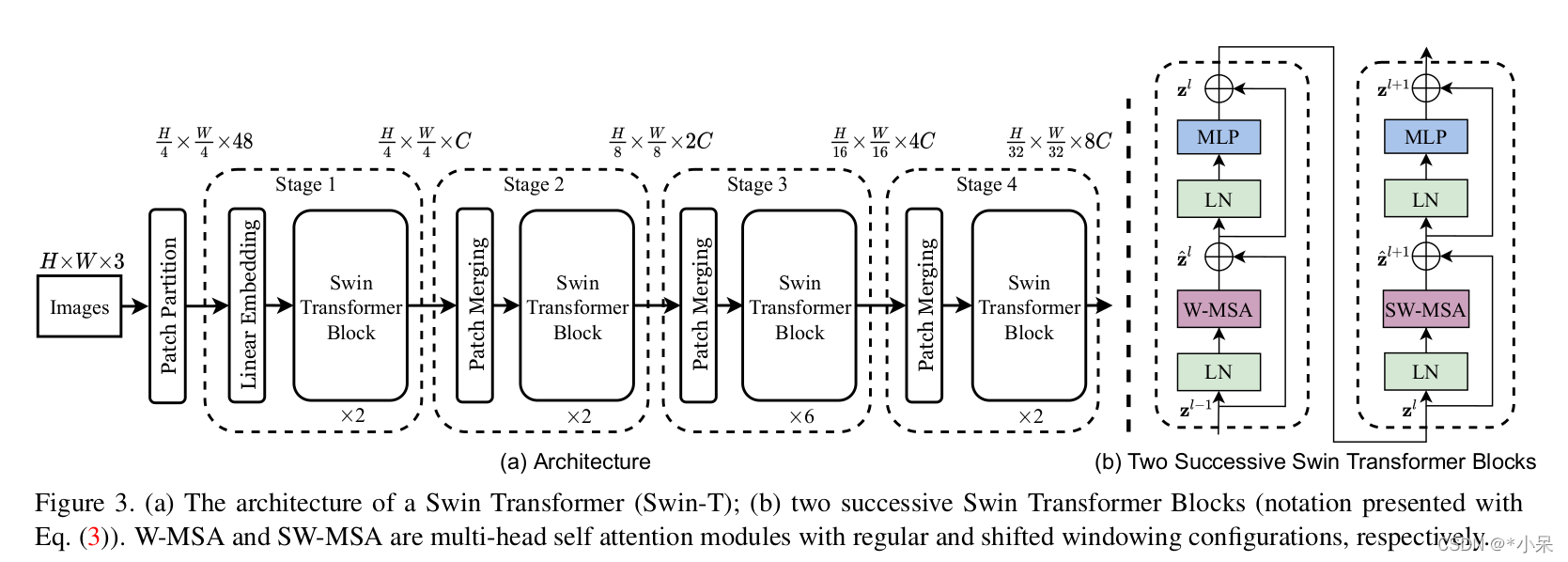
基本模块 BasicLayer
Swin-b 主体部分网络结构 BasicLayer
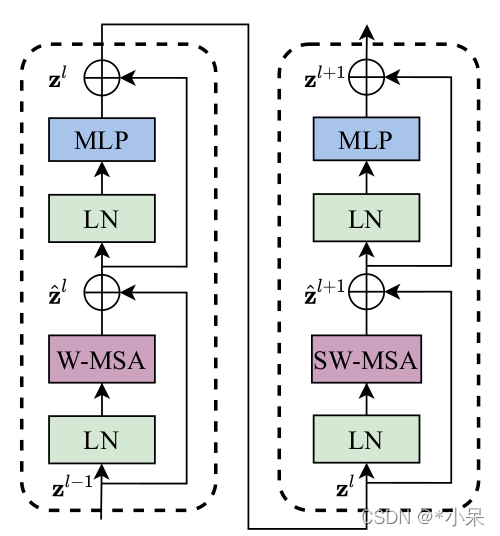
结构展示
BasicLayer(
(blocks): ModuleList(
(0): SwinTransformerBlock(
(norm1): LayerNorm((128,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
# WindowAttention
(attn): WindowAttention(
(qkv): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=384, bias=True)
(attn_drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(proj): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=128, bias=True)
(proj_drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=-1)
)
(drop_path): Identity()
(norm2): LayerNorm((128,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(mlp): Mlp(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=512, bias=True)
(act): GELU()
(fc2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=128, bias=True)
(drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
)
)
(1): SwinTransformerBlock(
(norm1): LayerNorm((128,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(attn): WindowAttention(
(qkv): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=384, bias=True)
(attn_drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(proj): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=128, bias=True)
(proj_drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=-1)
)
(drop_path): DropPath()
(norm2): LayerNorm((128,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(mlp): Mlp(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=512, bias=True)
(act): GELU()
(fc2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=128, bias=True)
(drop): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(downsample): PatchMerging(
(reduction): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=256, bias=False)
(norm): LayerNorm((512,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
)
Vit方式的 non-overlap patch partition 模块
先padding到patch尺寸的整数倍
if W % self.patch_size[1] != 0:
x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1]))
if H % self.patch_size[0] != 0:
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0]))
最核心的就是使用一个有 stride的 conv代替分 patch操作。
#using a nxn (s=n) conv is equivalent to splitting nxn (no overlap) patches.
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
else:
self.norm = None
编码得到的feature就是patch编码得到的了。
划分 windows 模块
得到了patch编码得到的embedding之后,以下面的方式,用window的方式进行划分,不同window放到batch轴上方便快速计算。
# partition windows, nW means number of windows
x_windows = window_partition(
shifted_x, self.window_size
) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C [392, 12, 12, 128]
x_windows = x_windows.view(
-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C
) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
WindowAttention 模块
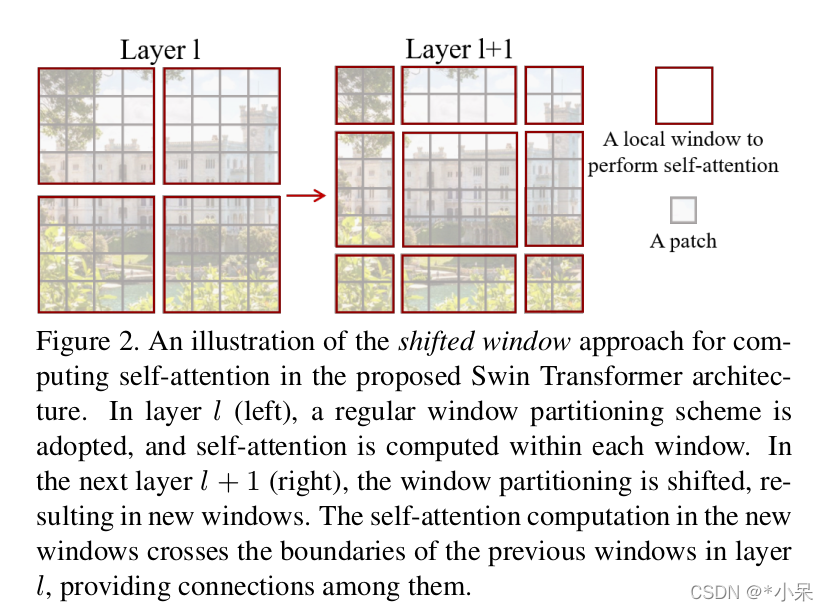
这里是swin 的精髓,作者也是对比了 global 计算affinity和 滑窗计算的复杂度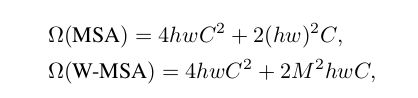
这里M是window size,常数。接下来讲解代码模块。
假设一些超参数
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww, (12, 12)
self.num_heads = num_heads # 4
head_dim = dim // num_heads # 32
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5 # 0.17
可学习的相对位置编码
创建一个 可学习的embedding, 尺寸为 [(2* Wh-1) * (2* Ww-1), nH] 。为什么尺寸是这样?是因为要look up table 也就是查表法得到某个位置的权重。这里解释一下,因为table需要囊括一个解空间,解空间(2* Wh-1) * (2* Ww-1)这么大,然后作为index,也就是下标,索引 这个relative_position_bias_table。比如两个embedding空间上相距10,那么就需要 找relative_position_bias_table [10], 相距-10,就是relative_position_bias_table [-10]。
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)
) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH (denotes num_heads)
相对位置表
需要产生一个 12 x 12 的window 的相对坐标编码,思考多大的解空间可以cover住相对位置那?当12x12的window,对于每一行简单用坐标位置差来描述的话,是 [-11, 11],也就是2w-1个值,正负是因为前后的相对位置不是无向的。目标矩阵尺寸是 (2w-1)x(2h-1)。好了,知道我们想干啥了就看代码了。
先得到一个 coords_flatten,尺寸是(2, Wh * Ww),W表示window。
tensor([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5,
6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7,
7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8,
9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]])
然后使用
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
coords_flatten[:, :, None] 维度是 [2, 144, 1], coords_flatten[:, None, :] 维度是[2, 1, 144]
两个矩阵对应相减, 根据广播规则得到相对的postion。relative_coords 尺寸 [2, 144,144]。广播规则可以这么看,固定coords_flatten[0]的第一个元素0,然后依次与coords_flatten[1] 的每一个元素相减。
tensor([[[ 0, 0, 0, ..., -11, -11, -11],
[ 0, 0, 0, ..., -11, -11, -11],
[ 0, 0, 0, ..., -11, -11, -11],
...,
[ 11, 11, 11, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 11, 11, 11, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 11, 11, 11, ..., 0, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, -1, -2, ..., -9, -10, -11],
[ 1, 0, -1, ..., -8, -9, -10],
[ 2, 1, 0, ..., -7, -8, -9],
...,
[ 9, 8, 7, ..., 0, -1, -2],
[ 10, 9, 8, ..., 1, 0, -1],
[ 11, 10, 9, ..., 2, 1, 0]]])
我们可以粗率计算下,最小是 0-11=-11,最大11-0=11,符合我们的预期,此时索引上面包含了很多负值。此时我们可以通过在每一个方向上+11抵消掉所有负数, 此时最大值是 22,最小值0.
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
在swin中,相对位置编码充当了B,也就是计算相似度时候的 bias。为了把上述的二维相对位置矩阵变成一维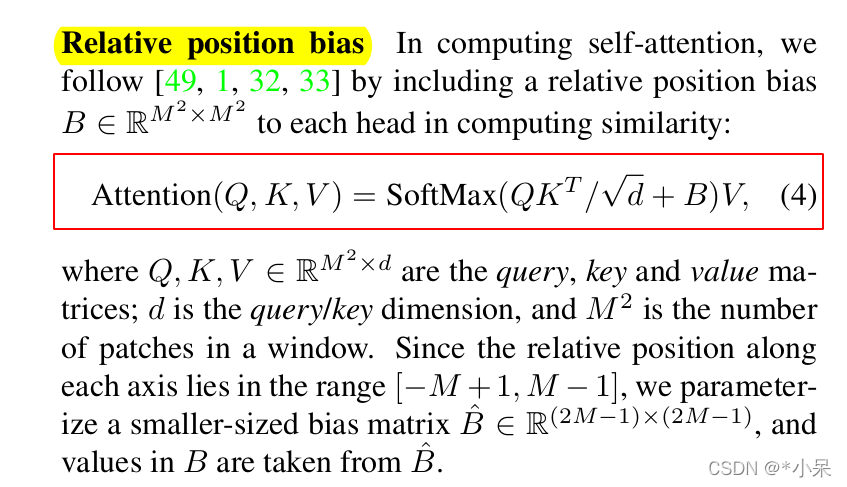 ,最简单的做法就是 i* (2w-1)+j 的编码方式。swin采用了一种高效的实现。
,最简单的做法就是 i* (2w-1)+j 的编码方式。swin采用了一种高效的实现。
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
# 下面的轴经过了 permute(1, 2, 0),把 2 放到了最后
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
所以最后的最大值就是 22 x (2x12-1) + 22 = 528, 最小值是0。注意这里w没变是12,而i, j 加了一个偏执11,所以变成了最大值22。
小结
再利用循环移位,就可以达到滑窗的目的。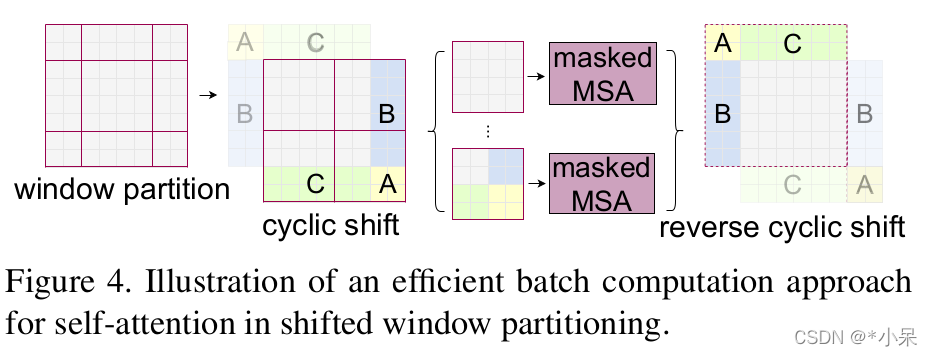
扩展:绝对位置编码
绝对位置编码使用的基本都是google17年发的那篇文章。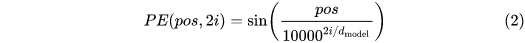
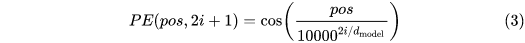
比如输入embedding 尺寸是[1, 512, 84, 128],输出位置编码 [1, 256, 21, 42] 。上面公式的pos 是按照行/列进行累积求和 然后归一化之后的向量, i 表示位置,比如256维度里面,偶数用sin编码,奇数索引用cos编码。相当于在channel 维度里 显式地融入了位置信息。
- 首先,相对于[1, 512, 84, 128]的1024 个 channel,position embedding 和 他们无关。
- 其次, [1, 256, 84, 128]的每一个channel 维度 (公式中的ℹ),表征了不同频率时候的正余弦信息。
为了更好理解,以y方向编码pos_y为例,我show一个case (c=0, 5)。 所以相当于每一个channel 都是一种绝对位置信息的编码。
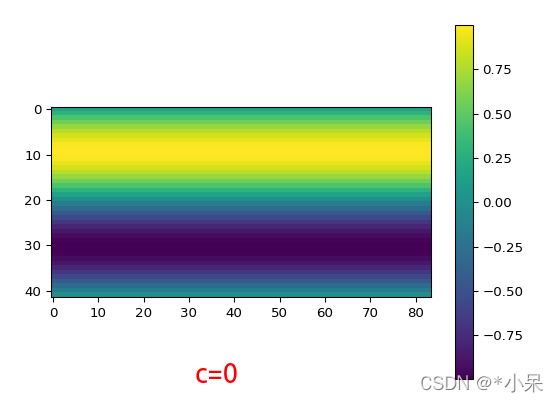
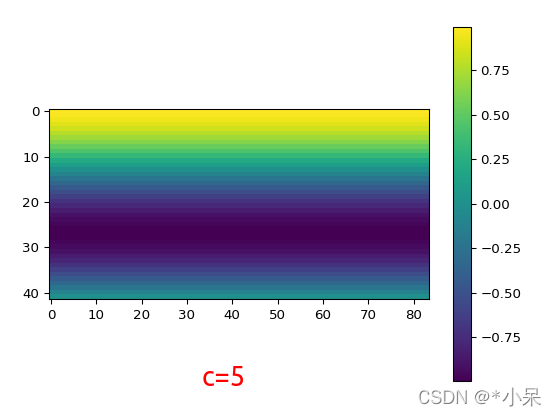
在hw上面方向,我随机sample了两个点,确实是sin形状函数曲线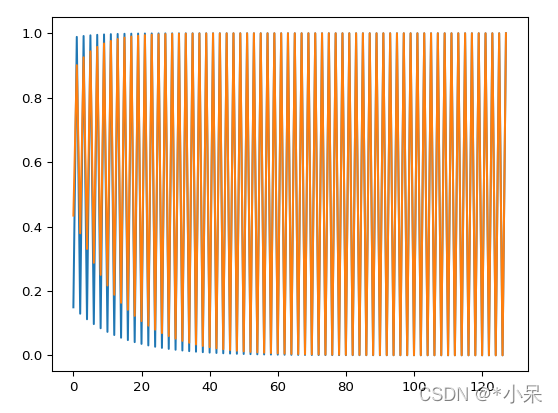
代码部分
# Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# # Modified by Bowen Cheng from: https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr/blob/master/models/position_encoding.py
"""
Various positional encodings for the transformer.
"""
import math
import torch
from torch import nn
class PositionEmbeddingSine(nn.Module):
"""
This is a more standard version of the position embedding, very similar to the one
used by the Attention is all you need paper, generalized to work on images.
"""
def __init__(self, num_pos_feats=64, temperature=10000, normalize=False, scale=None):
super().__init__()
self.num_pos_feats = num_pos_feats # half of the length of the embedding
self.temperature = temperature
self.normalize = normalize
if scale is not None and normalize is False:
raise ValueError("normalize should be True if scale is passed")
if scale is None:
scale = 2 * math.pi
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, x, mask=None): # x shape [1, 1024, 21, 42]
if mask is None:
mask = torch.zeros((x.size(0), x.size(2), x.size(3)), device=x.device, dtype=torch.bool)
not_mask = ~mask # [1, 21, 42]
y_embed = not_mask.cumsum(1, dtype=torch.float32) # Accumulate by column
x_embed = not_mask.cumsum(2, dtype=torch.float32) # Accumulate by row
# normalization by dividing maximum value
if self.normalize:
eps = 1e-6
# y_embed[:, -1:, :] dentoes maximum value of y, x is the same
y_embed = y_embed / (y_embed[:, -1:, :] + eps) * self.scale # [1, 21, 42]
x_embed = x_embed / (x_embed[:, :, -1:] + eps) * self.scale
dim_t = torch.arange(self.num_pos_feats, dtype=torch.float32, device=x.device) # 128
dim_t = self.temperature ** (2 * (dim_t // 2) / self.num_pos_feats) # 1-> 8.659e+3
pos_x = x_embed[:, :, :, None] / dim_t
pos_y = y_embed[:, :, :, None] / dim_t
pos_x = torch.stack(
(pos_x[:, :, :, 0::2].sin(), pos_x[:, :, :, 1::2].cos()), dim=4 # step 2
).flatten(3)
pos_y = torch.stack(
(pos_y[:, :, :, 0::2].sin(), pos_y[:, :, :, 1::2].cos()), dim=4
).flatten(3)
pos = torch.cat((pos_y, pos_x), dim=3).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return pos
def __repr__(self, _repr_indent=4):
head = "Positional encoding " + self.__class__.__name__
body = [
"num_pos_feats: {}".format(self.num_pos_feats),
"temperature: {}".format(self.temperature),
"normalize: {}".format(self.normalize),
"scale: {}".format(self.scale),
]
# _repr_indent = 4
lines = [head] + [" " * _repr_indent + line for line in body]
return "\n".join(lines)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)