揭秘大模型驱动的三重角色的万字长文翻译智能体的实现逻辑
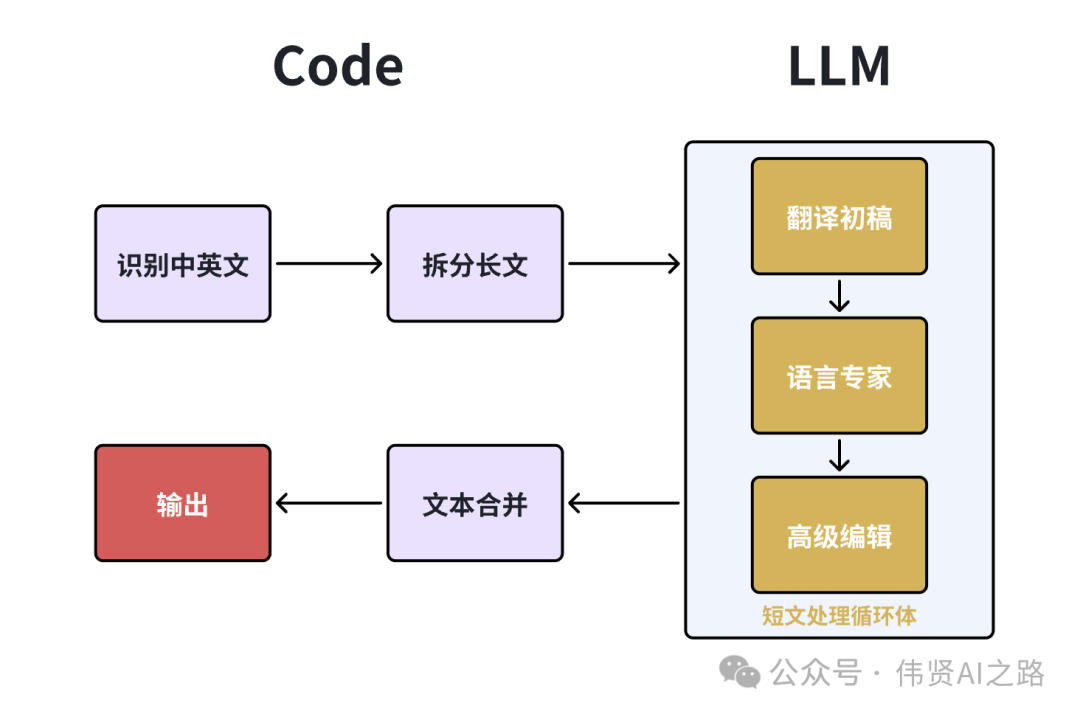
在如何用 AI 大模型打造三位一体的智能翻译神器?文章里已经实现了翻译初稿、语言专家译审、高级编辑汇总输出。但由于大模型处理输出的长度限制,针对万字以上的长文翻译结果是会被截短,所以需要拆分成多段短文来翻译,最终达成万字长文的翻译效果。
在 如何用 AI 大模型打造三位一体的智能翻译神器?文章里已经实现了翻译初稿、语言专家译审、高级编辑汇总输出。但由于大模型处理输出的长度限制,针对万字以上的长文翻译结果是会被截短,所以需要拆分成多段短文来翻译,最终达成万字长文的翻译效果。
下面跟着我的教程,动手实现一个处理上万字的长文翻译智能体吧。
新建智能体并添加工作流
在 Coze 平台创建智能体,编排选择“单 Agent(工作流模型)”,然后点击添加工作流。
识别中英互译的需求
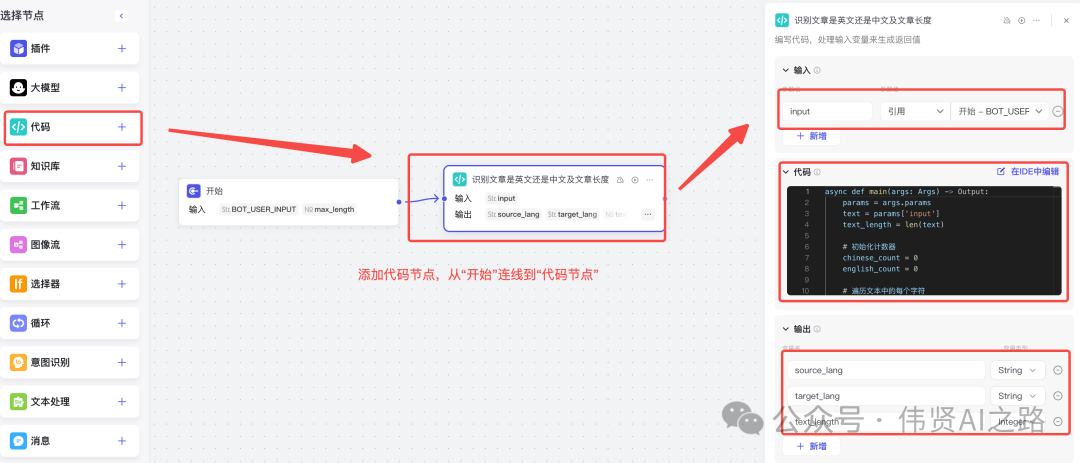
添加代码节点,从“开始”连线到“代码节点”,然后调整输入与输出参数名。
代码编写直接使用内置 AI 进行辅助编写,Python 代码参考如下:
async def main(args: Args) -> Output:
params = args.params
text = params['input']
text_length = len(text)
# 初始化计数器
chinese_count = 0
english_count = 0
# 遍历文本中的每个字符
for char in text:
# 判断是否为英文字母
if 'a' <= char.lower() <= 'z': # 使用lower()简化大小写判断
english_count += 1
if english_count > 1000:
return {'text_length':text_length, 'source_lang': '英文', 'target_lang': '中文'}
# 判断是否为中文字符
elif '\u4e00' <= char <= '\u9fff':
chinese_count += 1
if chinese_count > 1000:
return {'text_length':text_length, 'source_lang': '中文', 'target_lang': '英文'}
# 根据字符数量判断语言并构建返回字典
if chinese_count > english_count:
return {'text_length':text_length, 'source_lang': '中文', 'target_lang': '英文'}
elif english_count >= chinese_count and english_count > 7: # 英文至少有一定数量
return {'text_length':text_length, 'source_lang': '英文', 'target_lang': '中文'}
else:
return {'text_length':text_length, 'source_lang': 'Mixed or Unclear', 'target_lang': '中文'}
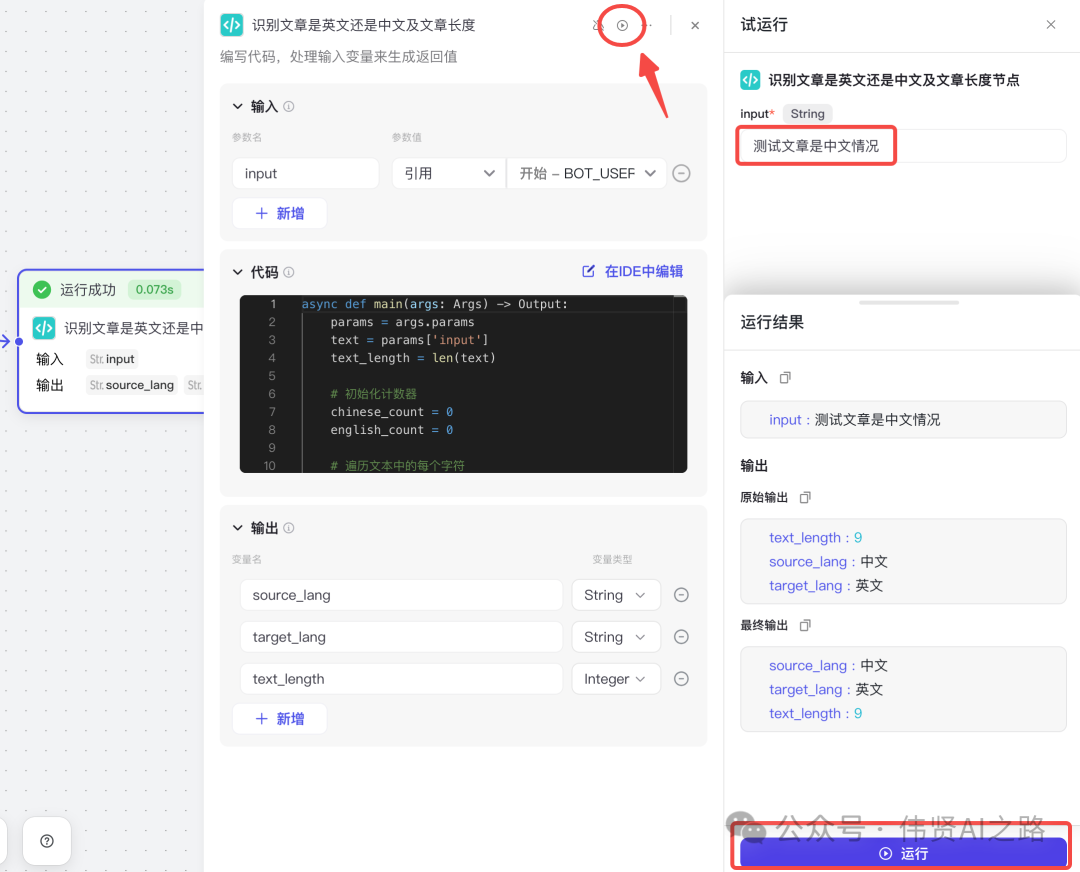
代码编写后都必须测试验证是否达预期,可以点击“测试该节点”,然后输入测试内容,验收输出结果。
长文使用代码拆分
和前面步骤一样,添加代码节点并与前节点连接,然后修改输入、输出参数,再添加代码并测试。
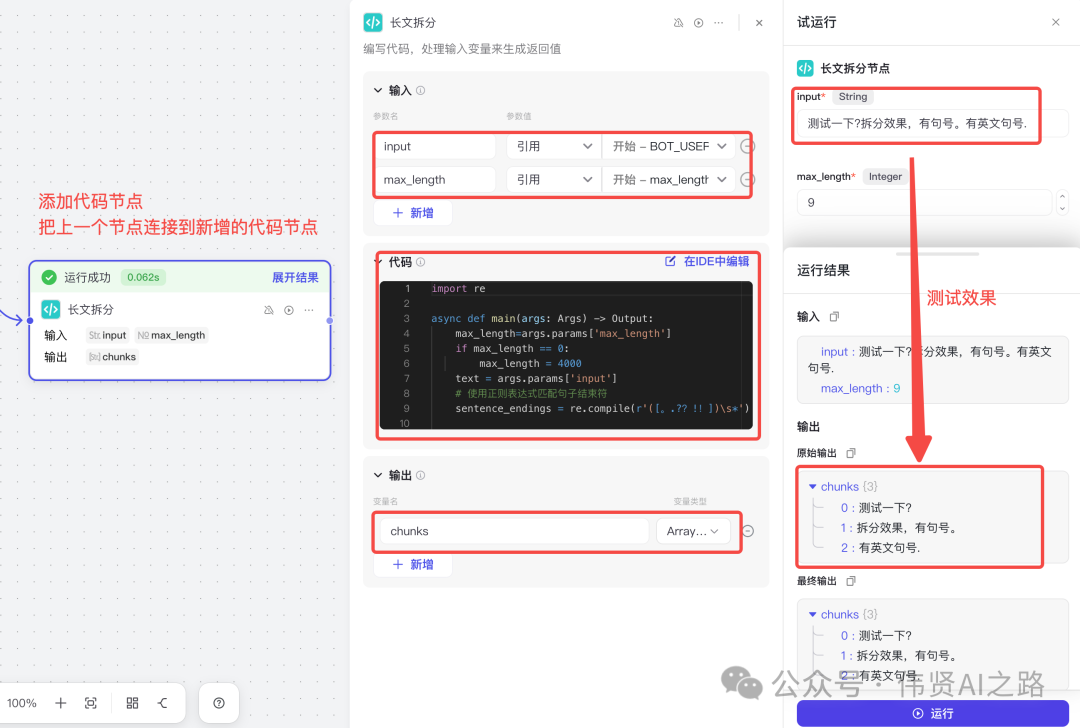
代码编写直接使用内置 AI 进行辅助编写,Python 代码参考如下:
import re
async def main(args: Args) -> Output:
max_length = 4000
text = args.params['input']
# 使用正则表达式匹配句子结束符
sentence_endings = re.compile(r'([。.??!!])\s*')
# 将文本分割成句子列表
sentences = sentence_endings.split(text)
chunks = []
current_chunk = ''
current_length = 0
for i, part in enumerate(sentences):
# 如果是句子结束符,直接添加到当前块
if i % 2 == 1: # 奇数索引是句子结束符
current_chunk += part
continue
# 计算当前句子长度
sentence_length = len(part)
# 如果加上当前句子后不超过最大长度
if current_length + sentence_length <= max_length:
current_chunk += part
current_length += sentence_length
else:
# 超过最大长度,保存当前块,并开始新的块
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(current_chunk.strip())
# 重置当前块和长度
current_chunk = part
current_length = sentence_length
# 如果当前句子本身超过了最大长度,继续分割该句子
while current_length > max_length:
# 在当前块中查找最近的句子结束符
match = re.search(r'[。.??!!]', current_chunk[:max_length])
if match:
# 在最近的句子结束符处分割
end_index = match.end()
chunks.append(current_chunk[:end_index].strip())
current_chunk = current_chunk[end_index:].lstrip()
current_length = len(current_chunk)
else:
# 如果仍然找不到句子结束符,直接截断
chunks.append(current_chunk[:max_length].strip())
current_chunk = current_chunk[max_length:].lstrip()
current_length = len(current_chunk)
# 添加最后一个块
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(current_chunk.strip())
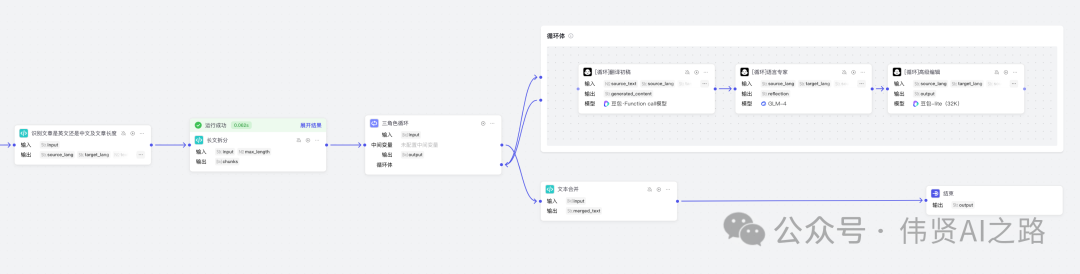
return {'chunks': chunks}循环体内增加 3 个大模型
选择“循环体”,点击大模型+按钮,循环体内会增加一个大模型节点,与 如何用 AI 大模型打造三位一体的智能翻译神器?的文章操作类似,依次添加翻译者(翻译初稿)、 语言专家(反思)、译审专家(把控翻译质量),具体的系统提示词、用户提示词请参考如何用 AI 大模型打造三位一体的智能翻译神器?原文。
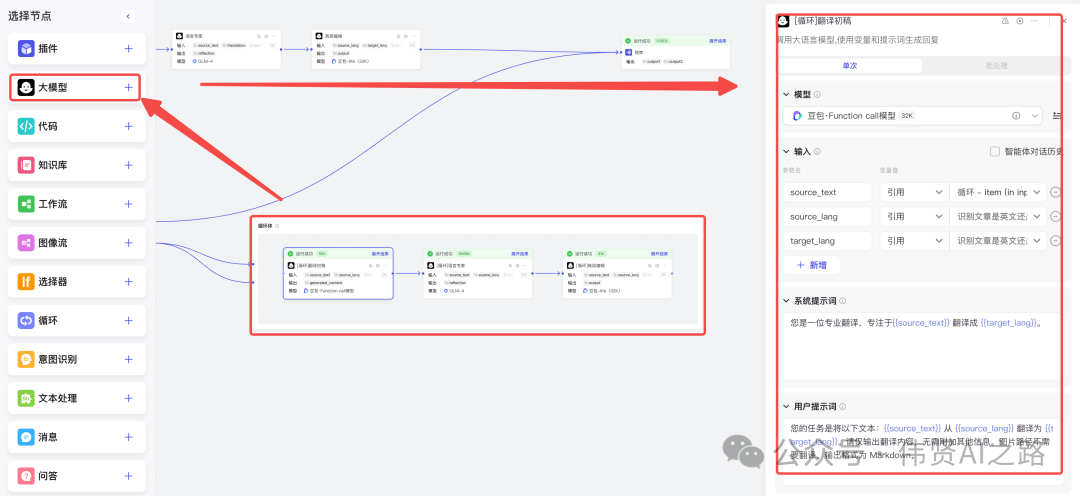
测试循环体执行效果如下,结果中会展示出循环次数,根据自己测试结果去调整长文拆分的长度。
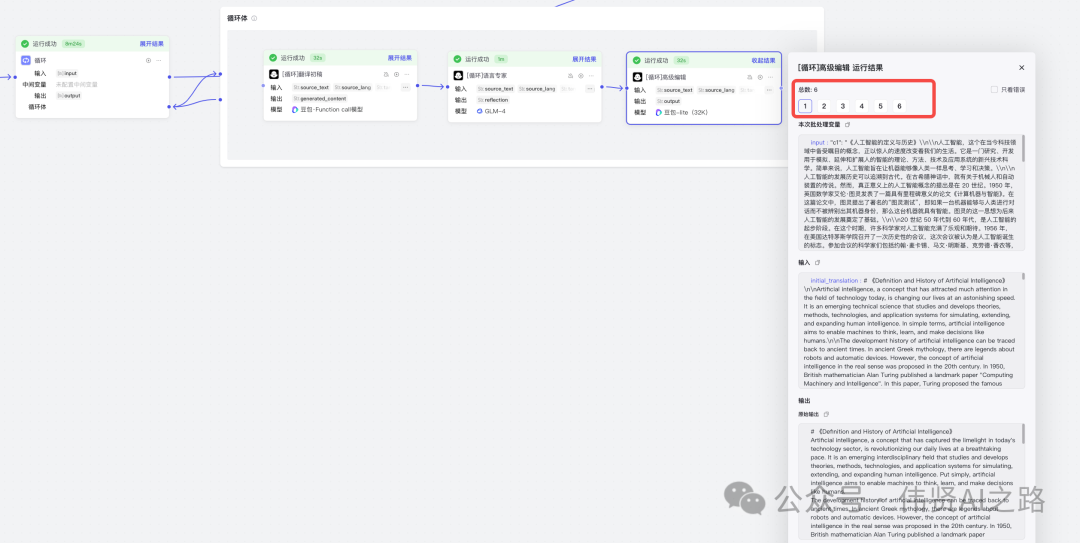
添加代码合并翻译结果
添加“代码”,与循环体节点连接上,然后添加代码实现翻译结果合并。
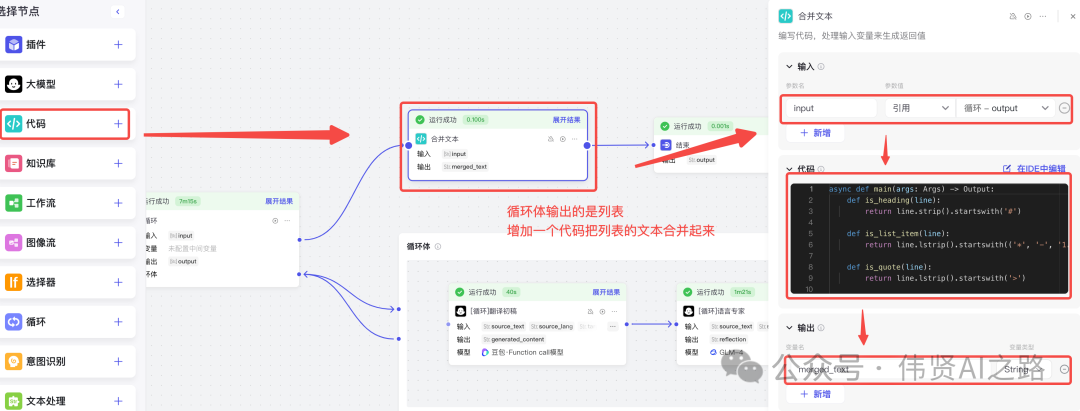
代码编写直接使用内置 AI 进行辅助编写,Python 代码参考如下:
async def main(args: Args) -> Output:
def is_heading(line):
return line.strip().startswith('#')
def is_list_item(line):
return line.lstrip().startswith(('*', '-', '1.'))
def is_quote(line):
return line.lstrip().startswith('>')
articles = args.params['input']
# 初始化合并后的文本
merged_text = ''
# 用于跟踪前一行是否是列表项或引用
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
# 遍历每个文章
for i, article in enumerate(articles):
# 去除文章两端的空白字符
article_lines = article.strip().splitlines()
for j, line in enumerate(article_lines):
# 如果不是第一个文章的第一行
if i > 0 and j == 0:
# 获取前一篇文章的最后一行
prev_last_line = articles[i - 1].strip().splitlines()[-1]
# 如果当前行和前一行都是列表项或引用
if (is_list_item(line) and is_list_item(prev_last_line)) or \
(is_quote(line) and is_quote(prev_last_line)):
# 直接连接
merged_text += '\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = True
# 如果当前行是列表项或引用,而前一行不是
elif (is_list_item(line) or is_quote(line)) and not (is_list_item(prev_last_line) or is_quote(prev_last_line)):
# 插入一个换行符
merged_text += '\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = True
# 如果当前行是普通文本,而前一行是列表项或引用
elif (not is_list_item(line) and not is_quote(line)) and (is_list_item(prev_last_line) or is_quote(prev_last_line)):
# 插入两个换行符
merged_text += '\n\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
# 如果当前行是标题
elif is_heading(line):
# 插入两个换行符
merged_text += '\n\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
else:
# 插入一个换行符
merged_text += '\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
else:
# 第一篇文章的第一行或同一文章的其他行
if j == 0:
merged_text += line
prev_is_list_or_quote = is_list_item(line) or is_quote(line)
else:
if (is_list_item(line) or is_quote(line)) and prev_is_list_or_quote:
# 直接连接
merged_text += '\n' + line
elif (is_list_item(line) or is_quote(line)) and not prev_is_list_or_quote:
# 插入一个换行符
merged_text += '\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = True
elif (not is_list_item(line) and not is_quote(line)) and prev_is_list_or_quote:
# 插入两个换行符
merged_text += '\n\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
elif is_heading(line):
# 插入两个换行符
merged_text += '\n\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
else:
# 插入一个换行符
merged_text += '\n' + line
prev_is_list_or_quote = False
return {"merged_text": merged_text}总结反思
现在实现逻辑是循环处理,耗时是非常久,可以考虑优化为并发处理,提升处理效率。
往期精彩
AI智能体实战|使用扣子Coze搭建AI智能体,看这一篇就够了(新手必读)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)