yolov8实例分割Tensorrt部署,onnx转engine部分示例详解(代码)
本文以yolov8的实例分割模型为例,对onnx转engine格式过程进行详解,方便大家在Tensorrt平台部署自己模型,通过示例帮助大家理解和应用。本文第一部分先对用到的代码进行讲解,应用部分每行都有注释,第二部分通过示例进行展示。在此之前应配置好ONNX和TensorRT库。
·
本文以yolov8的实例分割模型为例,对onnx转engine格式过程进行详解,方便大家在Tensorrt平台部署自己模型,通过示例帮助大家理解和应用。本文第一部分先对用到的代码进行讲解,应用部分每行都有注释,第二部分通过示例进行展示。
在此之前应配置好ONNX和TensorRT库。
代码
main()
本部分是主要代码,每行都有注释。main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "logging.h"
#include "NvOnnxParser.h"
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include <fstream>
/**********************/
/*加载库文件和*/
/**********************/
using namespace nvinfer1;
using namespace nvonnxparser;
//在终端运行时输入两个参数,分别是onnx文件位置和engine文件要保存的位置
static Logger gLogger;
int main(int argc,char** argv) {
//如果输入的参数小于2,则根据下面路径读取相应的参数
if (argc < 2) {
argv[1] = "../1.onnx";
argv[2] = "../1.engine";
}
//这个函数接收一个Logger对象gLogger作为参数,返回一个IBuilder对象,即推理构建器。
IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger);
//将数字 1(作为 uint32_t 类型)左移
const auto explicitBatch = 1U << static_cast<uint32_t>(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH);
//explicitBatch是一个布尔值参数,指示是否显式地在网络中包含批处理维度
INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(explicitBatch);
//ONNX解析器库来创建一个解析器对象
nvonnxparser::IParser* parser = nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, gLogger);
//加载onnx模型
const char* onnx_filename = argv[1];
//解析模型,并且只记录警告级别及以上的日志
parser->parseFromFile(onnx_filename, static_cast<int>(Logger::Severity::kWARNING));
//getNbErrors方法返回在解析过程中遇到的错误数量。
for (int i = 0; i < parser->getNbErrors(); ++i)
{
//打印错误信息
std::cout << parser->getError(i)->desc() << std::endl;
}
//成功加载和解析onnx模型
std::cout << "successfully load the onnx model" << std::endl;
//定义最大批次
unsigned int maxBatchSize = 1;
//// 设置最大批处理大小为
builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize);
//创建一个新的配置对象
IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig();
//设置最大工作空间
config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20);
//在构建过程中使用16位浮点数精度
config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kFP16);
//根据给定的网络(network)和配置(config)构建一个TensorRT引擎(engine)
ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config);
//尝试序列化一个引擎模型。engine->serialize()方法被用来将TensorRT引擎模型转换为可以存储或传输的格式。
IHostMemory *gieModelStream = engine->serialize();
std::ofstream p(argv[2], std::ios::binary);
if (!p)
{
std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//gieModelStream->size()返回要写入的数据的大小(以字节为单位)
//reinterpret_cast<const char*>(gieModelStream->data())将gieModelStream->data()
//的返回值转换为一个指向const char*类型的指针,该指针指向要写入的数据的起始位置
p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(gieModelStream->data()), gieModelStream->size());
//销毁流,释放内存
gieModelStream->destroy();
std::cout << "successfully generate the trt engine model" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
logging.h
下面是logging.h代码,此部分是通用,便没有注释,直接使用即可。logging.h
/*
* Copyright (c) 2019, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#ifndef TENSORRT_LOGGING_H
#define TENSORRT_LOGGING_H
#include "NvInferRuntimeCommon.h"
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using Severity = nvinfer1::ILogger::Severity;
class LogStreamConsumerBuffer : public std::stringbuf
{
public:
LogStreamConsumerBuffer(std::ostream& stream, const std::string& prefix, bool shouldLog)
: mOutput(stream)
, mPrefix(prefix)
, mShouldLog(shouldLog)
{
}
LogStreamConsumerBuffer(LogStreamConsumerBuffer&& other)
: mOutput(other.mOutput)
{
}
~LogStreamConsumerBuffer()
{
// std::streambuf::pbase() gives a pointer to the beginning of the buffered part of the output sequence
// std::streambuf::pptr() gives a pointer to the current position of the output sequence
// if the pointer to the beginning is not equal to the pointer to the current position,
// call putOutput() to log the output to the stream
if (pbase() != pptr())
{
putOutput();
}
}
// synchronizes the stream buffer and returns 0 on success
// synchronizing the stream buffer consists of inserting the buffer contents into the stream,
// resetting the buffer and flushing the stream
virtual int sync()
{
putOutput();
return 0;
}
void putOutput()
{
if (mShouldLog)
{
// prepend timestamp
std::time_t timestamp = std::time(nullptr);
tm* tm_local = std::localtime(×tamp);
std::cout << "[";
std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << 1 + tm_local->tm_mon << "/";
std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_mday << "/";
std::cout << std::setw(4) << std::setfill('0') << 1900 + tm_local->tm_year << "-";
std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_hour << ":";
std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_min << ":";
std::cout << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << tm_local->tm_sec << "] ";
// std::stringbuf::str() gets the string contents of the buffer
// insert the buffer contents pre-appended by the appropriate prefix into the stream
mOutput << mPrefix << str();
// set the buffer to empty
str("");
// flush the stream
mOutput.flush();
}
}
void setShouldLog(bool shouldLog)
{
mShouldLog = shouldLog;
}
private:
std::ostream& mOutput;
std::string mPrefix;
bool mShouldLog;
};
//!
//! \class LogStreamConsumerBase
//! \brief Convenience object used to initialize LogStreamConsumerBuffer before std::ostream in LogStreamConsumer
//!
class LogStreamConsumerBase
{
public:
LogStreamConsumerBase(std::ostream& stream, const std::string& prefix, bool shouldLog)
: mBuffer(stream, prefix, shouldLog)
{
}
protected:
LogStreamConsumerBuffer mBuffer;
};
//!
//! \class LogStreamConsumer
//! \brief Convenience object used to facilitate use of C++ stream syntax when logging messages.
//! Order of base classes is LogStreamConsumerBase and then std::ostream.
//! This is because the LogStreamConsumerBase class is used to initialize the LogStreamConsumerBuffer member field
//! in LogStreamConsumer and then the address of the buffer is passed to std::ostream.
//! This is necessary to prevent the address of an uninitialized buffer from being passed to std::ostream.
//! Please do not change the order of the parent classes.
//!
class LogStreamConsumer : protected LogStreamConsumerBase, public std::ostream
{
public:
//! \brief Creates a LogStreamConsumer which logs messages with level severity.
//! Reportable severity determines if the messages are severe enough to be logged.
LogStreamConsumer(Severity reportableSeverity, Severity severity)
: LogStreamConsumerBase(severityOstream(severity), severityPrefix(severity), severity <= reportableSeverity)
, std::ostream(&mBuffer) // links the stream buffer with the stream
, mShouldLog(severity <= reportableSeverity)
, mSeverity(severity)
{
}
LogStreamConsumer(LogStreamConsumer&& other)
: LogStreamConsumerBase(severityOstream(other.mSeverity), severityPrefix(other.mSeverity), other.mShouldLog)
, std::ostream(&mBuffer) // links the stream buffer with the stream
, mShouldLog(other.mShouldLog)
, mSeverity(other.mSeverity)
{
}
void setReportableSeverity(Severity reportableSeverity)
{
mShouldLog = mSeverity <= reportableSeverity;
mBuffer.setShouldLog(mShouldLog);
}
private:
static std::ostream& severityOstream(Severity severity)
{
return severity >= Severity::kINFO ? std::cout : std::cerr;
}
static std::string severityPrefix(Severity severity)
{
switch (severity)
{
case Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR: return "[F] ";
case Severity::kERROR: return "[E] ";
case Severity::kWARNING: return "[W] ";
case Severity::kINFO: return "[I] ";
case Severity::kVERBOSE: return "[V] ";
default: assert(0); return "";
}
}
bool mShouldLog;
Severity mSeverity;
};
//! \class Logger
//!
//! \brief Class which manages logging of TensorRT tools and samples
//!
//! \details This class provides a common interface for TensorRT tools and samples to log information to the console,
//! and supports logging two types of messages:
//!
//! - Debugging messages with an associated severity (info, warning, error, or internal error/fatal)
//! - Test pass/fail messages
//!
//! The advantage of having all samples use this class for logging as opposed to emitting directly to stdout/stderr is
//! that the logic for controlling the verbosity and formatting of sample output is centralized in one location.
//!
//! In the future, this class could be extended to support dumping test results to a file in some standard format
//! (for example, JUnit XML), and providing additional metadata (e.g. timing the duration of a test run).
//!
//! TODO: For backwards compatibility with existing samples, this class inherits directly from the nvinfer1::ILogger
//! interface, which is problematic since there isn't a clean separation between messages coming from the TensorRT
//! library and messages coming from the sample.
//!
//! In the future (once all samples are updated to use Logger::getTRTLogger() to access the ILogger) we can refactor the
//! class to eliminate the inheritance and instead make the nvinfer1::ILogger implementation a member of the Logger
//! object.
class Logger : public nvinfer1::ILogger
{
public:
Logger(Severity severity = Severity::kWARNING)
: mReportableSeverity(severity)
{
}
//!
//! \enum TestResult
//! \brief Represents the state of a given test
//!
enum class TestResult
{
kRUNNING, //!< The test is running
kPASSED, //!< The test passed
kFAILED, //!< The test failed
kWAIVED //!< The test was waived
};
//!
//! \brief Forward-compatible method for retrieving the nvinfer::ILogger associated with this Logger
//! \return The nvinfer1::ILogger associated with this Logger
//!
//! TODO Once all samples are updated to use this method to register the logger with TensorRT,
//! we can eliminate the inheritance of Logger from ILogger
//!
nvinfer1::ILogger& getTRTLogger()
{
return *this;
}
//!
//! \brief Implementation of the nvinfer1::ILogger::log() virtual method
//!
//! Note samples should not be calling this function directly; it will eventually go away once we eliminate the
//! inheritance from nvinfer1::ILogger
//!
void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override
{
LogStreamConsumer(mReportableSeverity, severity) << "[TRT] " << std::string(msg) << std::endl;
}
//!
//! \brief Method for controlling the verbosity of logging output
//!
//! \param severity The logger will only emit messages that have severity of this level or higher.
//!
void setReportableSeverity(Severity severity)
{
mReportableSeverity = severity;
}
//!
//! \brief Opaque handle that holds logging information for a particular test
//!
//! This object is an opaque handle to information used by the Logger to print test results.
//! The sample must call Logger::defineTest() in order to obtain a TestAtom that can be used
//! with Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().
//!
class TestAtom
{
public:
TestAtom(TestAtom&&) = default;
private:
friend class Logger;
TestAtom(bool started, const std::string& name, const std::string& cmdline)
: mStarted(started)
, mName(name)
, mCmdline(cmdline)
{
}
bool mStarted;
std::string mName;
std::string mCmdline;
};
//!
//! \brief Define a test for logging
//!
//! \param[in] name The name of the test. This should be a string starting with
//! "TensorRT" and containing dot-separated strings containing
//! the characters [A-Za-z0-9_].
//! For example, "TensorRT.sample_googlenet"
//! \param[in] cmdline The command line used to reproduce the test
//
//! \return a TestAtom that can be used in Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().
//!
static TestAtom defineTest(const std::string& name, const std::string& cmdline)
{
return TestAtom(false, name, cmdline);
}
//!
//! \brief A convenience overloaded version of defineTest() that accepts an array of command-line arguments
//! as input
//!
//! \param[in] name The name of the test
//! \param[in] argc The number of command-line arguments
//! \param[in] argv The array of command-line arguments (given as C strings)
//!
//! \return a TestAtom that can be used in Logger::reportTest{Start,End}().
static TestAtom defineTest(const std::string& name, int argc, char const* const* argv)
{
auto cmdline = genCmdlineString(argc, argv);
return defineTest(name, cmdline);
}
//!
//! \brief Report that a test has started.
//!
//! \pre reportTestStart() has not been called yet for the given testAtom
//!
//! \param[in] testAtom The handle to the test that has started
//!
static void reportTestStart(TestAtom& testAtom)
{
reportTestResult(testAtom, TestResult::kRUNNING);
assert(!testAtom.mStarted);
testAtom.mStarted = true;
}
//!
//! \brief Report that a test has ended.
//!
//! \pre reportTestStart() has been called for the given testAtom
//!
//! \param[in] testAtom The handle to the test that has ended
//! \param[in] result The result of the test. Should be one of TestResult::kPASSED,
//! TestResult::kFAILED, TestResult::kWAIVED
//!
static void reportTestEnd(const TestAtom& testAtom, TestResult result)
{
assert(result != TestResult::kRUNNING);
assert(testAtom.mStarted);
reportTestResult(testAtom, result);
}
static int reportPass(const TestAtom& testAtom)
{
reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kPASSED);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
static int reportFail(const TestAtom& testAtom)
{
reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kFAILED);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
static int reportWaive(const TestAtom& testAtom)
{
reportTestEnd(testAtom, TestResult::kWAIVED);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
static int reportTest(const TestAtom& testAtom, bool pass)
{
return pass ? reportPass(testAtom) : reportFail(testAtom);
}
Severity getReportableSeverity() const
{
return mReportableSeverity;
}
private:
//!
//! \brief returns an appropriate string for prefixing a log message with the given severity
//!
static const char* severityPrefix(Severity severity)
{
switch (severity)
{
case Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR: return "[F] ";
case Severity::kERROR: return "[E] ";
case Severity::kWARNING: return "[W] ";
case Severity::kINFO: return "[I] ";
case Severity::kVERBOSE: return "[V] ";
default: assert(0); return "";
}
}
//!
//! \brief returns an appropriate string for prefixing a test result message with the given result
//!
static const char* testResultString(TestResult result)
{
switch (result)
{
case TestResult::kRUNNING: return "RUNNING";
case TestResult::kPASSED: return "PASSED";
case TestResult::kFAILED: return "FAILED";
case TestResult::kWAIVED: return "WAIVED";
default: assert(0); return "";
}
}
//!
//! \brief returns an appropriate output stream (cout or cerr) to use with the given severity
//!
static std::ostream& severityOstream(Severity severity)
{
return severity >= Severity::kINFO ? std::cout : std::cerr;
}
//!
//! \brief method that implements logging test results
//!
static void reportTestResult(const TestAtom& testAtom, TestResult result)
{
severityOstream(Severity::kINFO) << "&&&& " << testResultString(result) << " " << testAtom.mName << " # "
<< testAtom.mCmdline << std::endl;
}
//!
//! \brief generate a command line string from the given (argc, argv) values
//!
static std::string genCmdlineString(int argc, char const* const* argv)
{
std::stringstream ss;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
{
if (i > 0)
ss << " ";
ss << argv[i];
}
return ss.str();
}
Severity mReportableSeverity;
};
namespace
{
//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kVERBOSE
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_VERBOSE(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_VERBOSE(const Logger& logger)
{
return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kVERBOSE);
}
//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kINFO
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_INFO(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_INFO(const Logger& logger)
{
return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kINFO);
}
//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kWARNING
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_WARN(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_WARN(const Logger& logger)
{
return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kWARNING);
}
//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kERROR
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_ERROR(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_ERROR(const Logger& logger)
{
return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kERROR);
}
//!
//! \brief produces a LogStreamConsumer object that can be used to log messages of severity kINTERNAL_ERROR
// ("fatal" severity)
//!
//! Example usage:
//!
//! LOG_FATAL(logger) << "hello world" << std::endl;
//!
inline LogStreamConsumer LOG_FATAL(const Logger& logger)
{
return LogStreamConsumer(logger.getReportableSeverity(), Severity::kINTERNAL_ERROR);
}
} // anonymous namespace
#endif // TENSORRT_LOGGING_H
CmakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(main)
#这是指定C++标准的一个标志,这里指定为C++11。
add_definitions(-std=c++11)
#添加了一个宏定义API_EXPORTS
add_definitions(-DAPI_EXPORTS)
#这行代码设置CMake的C++标准为11。这样,CMake会知道在编译C++代码时使用C++11标准
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
#这行代码设置了构建类型为Debug。这意味着在编译时将启用额外的调试信息。
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
#设置了CUDA编译器的路径
set(CMAKE_CUDA_COMPILER /usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc)
#这行代码启用了CUDA语言的支持。这样,CMake会知道在构建过程中处理CUDA源代码
enable_language(CUDA)
# include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different
#判断平台系统架构是否为aarch64,选择相应的cuda和tensorrt路径
if (CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR MATCHES "aarch64")
message("embed_platform on")
include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/targets/aarch64-linux/include)
link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/targets/aarch64-linux/lib)
else()
message("embed_platform off")
#下面的路径可以根据自己情况修改
# cuda
include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include)
link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64)
# tensorrt
include_directories(/home/lindsay/TensorRT-8.4.1.5/include)
link_directories(/home/lindsay/TensorRT-8.4.1.5/lib)
endif()
#添加opencv路径
find_package(OpenCV)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
#生成一个可执行文件main,根据main.cpp的源码内容
add_executable(main ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cpp)
#将nvinfer库链接到main可执行文件
target_link_libraries(main nvinfer)
target_link_libraries(main nvonnxparser)
target_link_libraries(main cudart)
target_link_libraries(main ${OpenCV_LIBS})
#-O2 是一个编译器优化标志,它告诉编译器进行所有支持的优化,除了空间优化。
#这将尝试提高代码运行的速度,而不考虑生成的二进制文件的大小。
#-pthread 是一个编译器选项,用于指示编译器生成适用于多线程环境的代码。
#如果你的代码是多线程的,或者你想让它支持多线程,那么这个选项是必要的。
#add_definitions 命令将这些标志添加到所有的源文件中,这意味着所有的源文件都将使用这些标志进行编译。
add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
示例
建立文件main.cpp、logging.h和CmakeLists.txt文件,内容如上面所述,并把onnx模型放在同一文件夹,如下图所示。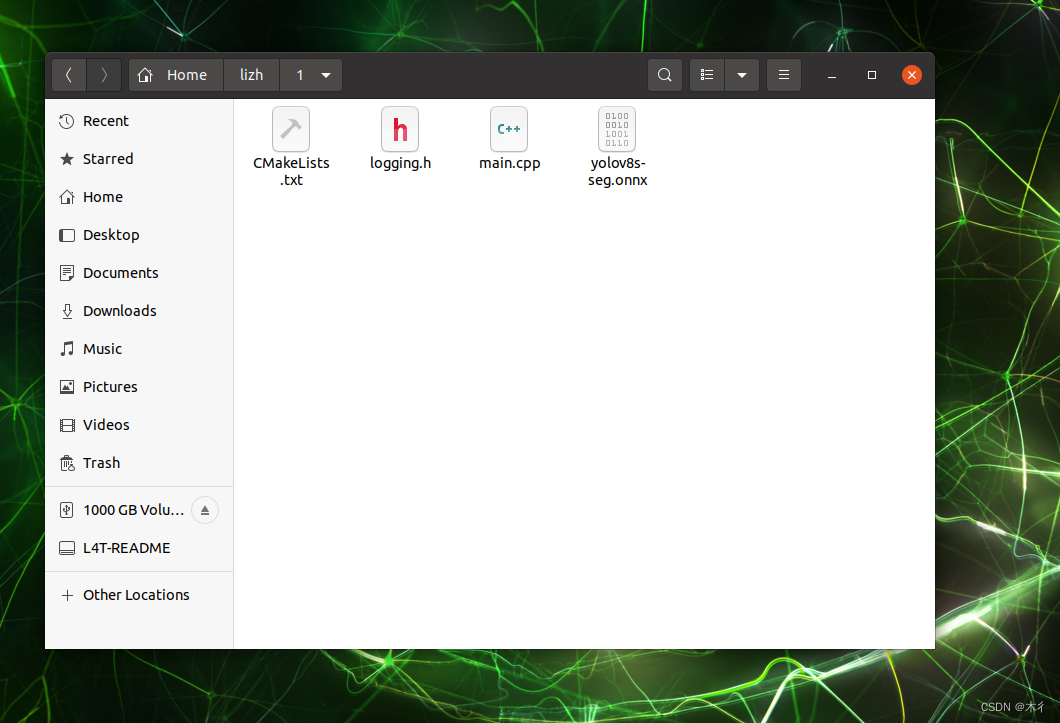
执行如下命令
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j32
./main ../yolov8s-seg.onnx yolov8s-seg.engine
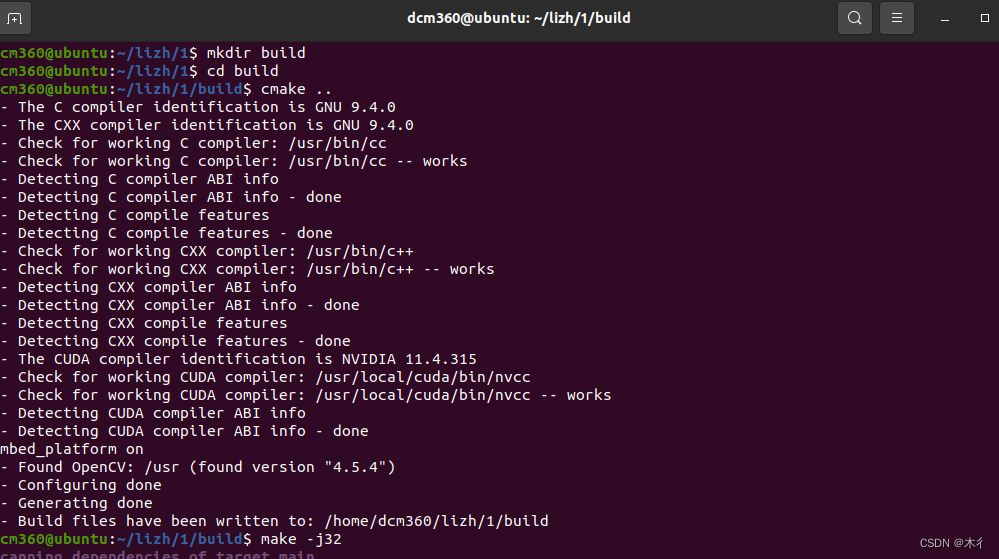
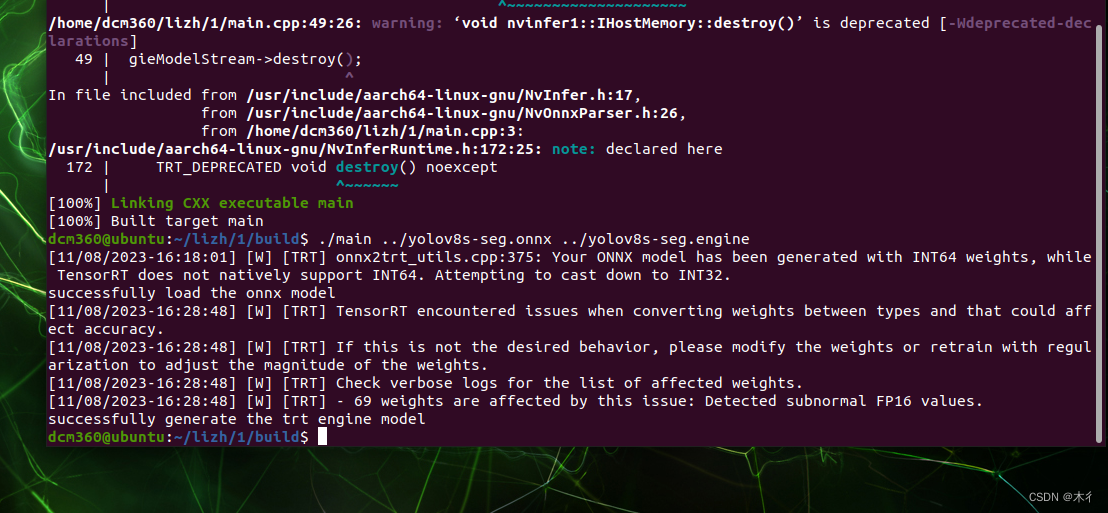
生成所需的engine文件,结合推理代码进行推理。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)