python 用YOLOv4模型识别物体
【代码】python 用YOLOv4模型识别物体。
·
效果
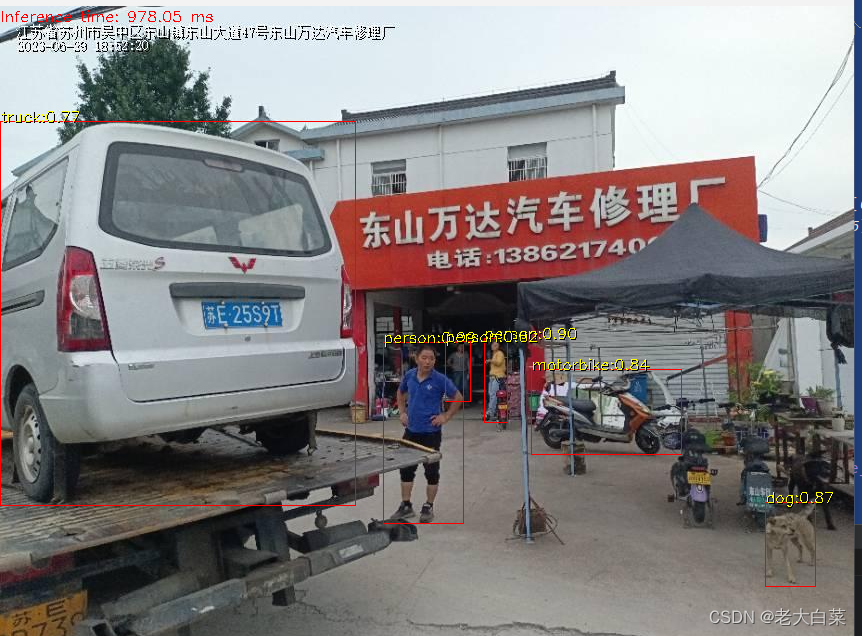 ###代码:
###代码:
# 导入OpenCV库,用于处理图像和视频
import cv2
# 为方便起见,将cv2重命名为cv
cv = cv2
# 导入numpy库,用于处理数组和矩阵
import numpy as np
# 导入time库,用于计算程序运行时间
import time
# 从Darknet配置和权重文件中读取YOLOv4模型
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet("yolov4.cfg", "yolov4.weights")
# 设置模型的后端为CUDA,即使用GPU进行计算
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
# 设置模型的目标为CUDA
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
# 设置置信度阈值,只有检测到的对象的置信度大于这个阈值,才会被认为是有效的检测
confThreshold = 0.5
# 设置非极大值抑制的阈值,用于消除冗余的重叠框
nmsThreshold = 0.4
# 读取待检测的图像
frame = cv2.imread("img_11.png")
# 设置类别标签文件路径
classesFile = "coco.names";
# 初始化类别列表
classes = None
# 打开类别标签文件,并读取所有类别标签,每个标签占一行
with open(classesFile, 'rt') as f:
classes = f.read().rstrip('\n').split('\n')
# 定义一个函数,用于获取模型的输出层名称
def getOutputsNames(net):
# 获取网络中所有层的名称
layersNames = net.getLayerNames()
# 获取输出层的名称,即没有连接输出的层的名称
return [layersNames[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# 打印模型的输出层名称
print(getOutputsNames(net))
# 定义一个函数,用于对模型的输出进行后处理,包括移除低置信度的边界框和使用非极大值抑制消除冗余框
def postprocess(frame, outs):
# 获取图像的高度和宽度
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
# 初始化类别ID、置信度和边界框的列表
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
# 遍历模型的每个输出,每个输出对应一种尺度的输入
for out in outs:
# 遍历输出的每个检测框
for detection in out:
# 获取检测框的置信度分数,长度为类别数+1(包括背景类)
scores = detection[5:]
# 获取最大置信度对应的类别ID
classId = np.argmax(scores)
# 获取该类别ID对应的置信度分数
confidence = scores[classId]
# 如果置信度大于阈值,则保留该检测框
if confidence > confThreshold:
# 计算检测框的中心点坐标和宽高(相对坐标)
center_x = int(detection[0] * frameWidth)
center_y = int(detection[1] * frameHeight)
width = int(detection[2] * frameWidth)
height = int(detection[3] * frameHeight)
# 计算检测框的左上角和右下角坐标(绝对坐标)
left = int(center_x - width / 2)
top = int(center_y - height / 2)
# 将类别ID、置信度和边界框坐标添加到列表中
classIds.append(classId)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
# 使用非极大值抑制消除冗余的重叠框,返回保留的框的索引列表
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold)
# 遍历保留的框的索引列表,绘制这些框并显示类别标签和置信度分数
for i in indices:
box = boxes[i]
left = box[0]
top = box[1]
width = box[2]
height = box[3]
drawPred(classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)
# 定义一个函数,用于在图像上绘制预测的边界框和类别标签及置信度分数
def drawPred(classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):
# 在图像上绘制一个红色的边界框
cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255))
# 设置类别标签的格式,包括置信度分数(保留两位小数)和类别名称两部分,中间用冒号分隔开来。
label = '%.2f' % conf
# Get the label for the class name and its confidence
if classes:
assert (classId < len(classes))
label = '%s:%s' % (classes[classId], label)
# Display the label at the top of the bounding box
labelSize, baseLine = cv.getTextSize(label, cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, labelSize[1])
cv.putText(frame, label, (left + 1, top + 1), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
cv.putText(frame, label, (left, top), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 255))
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255, (416, 416), [0, 0, 0], 1, crop=False)
t1 = time.time()
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(getOutputsNames(net))
print(time.time() - t1)
postprocess(frame, outs)
t, _ = net.getPerfProfile()
label = 'Inference time: %.2f ms' % (t * 1000.0 / cv.getTickFrequency())
cv.putText(frame, label, (0, 15), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255))
cv2.imshow("result", frame)
cv2.waitKey(0)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献14条内容
已为社区贡献14条内容







所有评论(0)