手势 识别
手势识别
·
小组做的一个基于mediapipe的手势识别
文章目录
前言
在基于mediapipe的基础上实现对手势的识别
一、mediapipe是什么?
MediaPipe是一个主要用于构建音频、视频或任何时间序列数据的框架。在 MediaPipe 框架的帮助下,我们可以为不同的媒体处理功能构建管道。可以看看这篇文章
二、使用步骤
1.引入库
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
from numpy import linalg2.定义手势函数
# 手指检测
def finger_stretch_detect(point1, point2, point3):
result = 0
# 计算向量的L2范数
dist1 = np.linalg.norm((point2 - point1), ord=2)
dist2 = np.linalg.norm((point3 - point1), ord=2)
if dist2 > dist1:
result = 1
return result
# 检测手势
def detect_hands_gesture(result):
if (result[0] == 1) and (result[1] == 0) and (result[2] == 0) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 0):
gesture = "good"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 1) and (result[2] == 0) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 0):
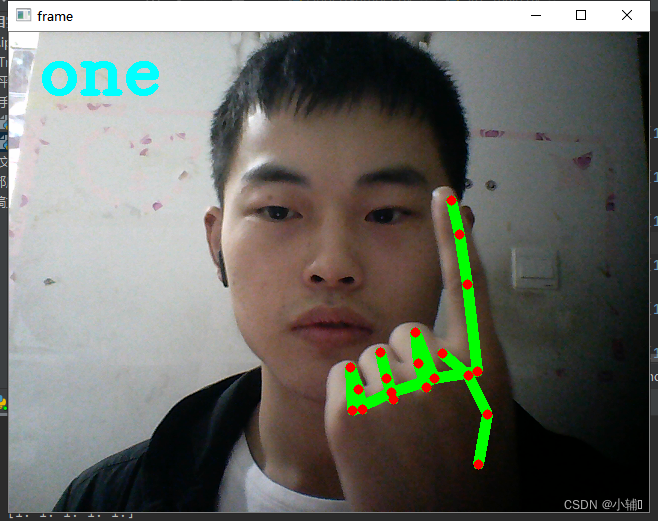
gesture = "one"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 0) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 0):
gesture = "what?"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 1) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 0):
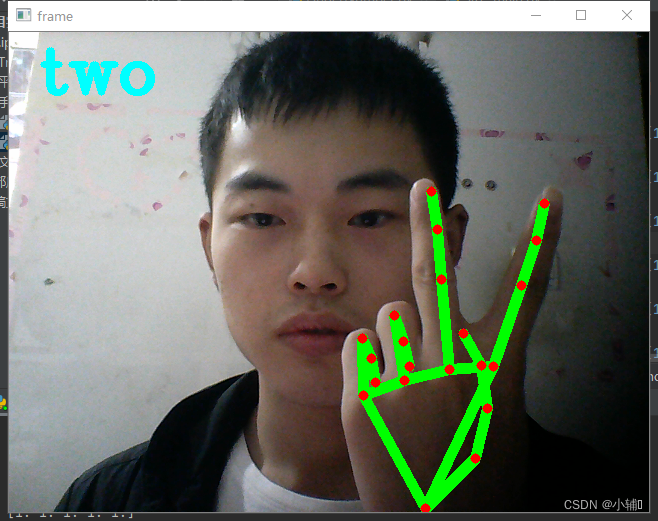
gesture = "two"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 1) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 1) and (result[4] == 0):
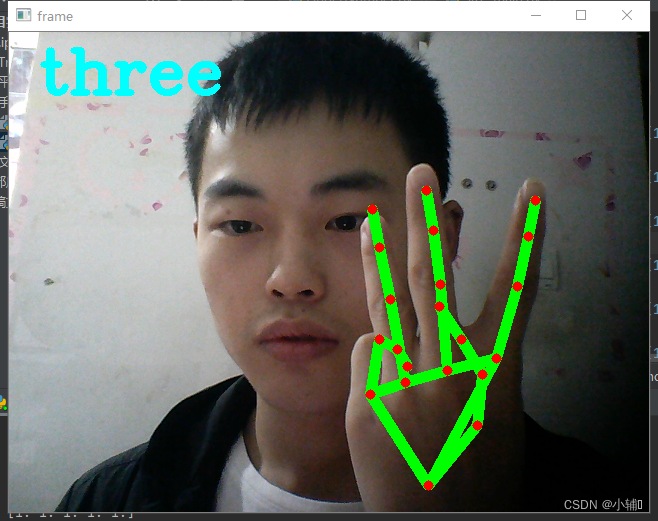
gesture = "three"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 1) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 1) and (result[4] == 1):
gesture = "four"
elif (result[0] == 1) and (result[1] == 1) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 1) and (result[4] == 1):
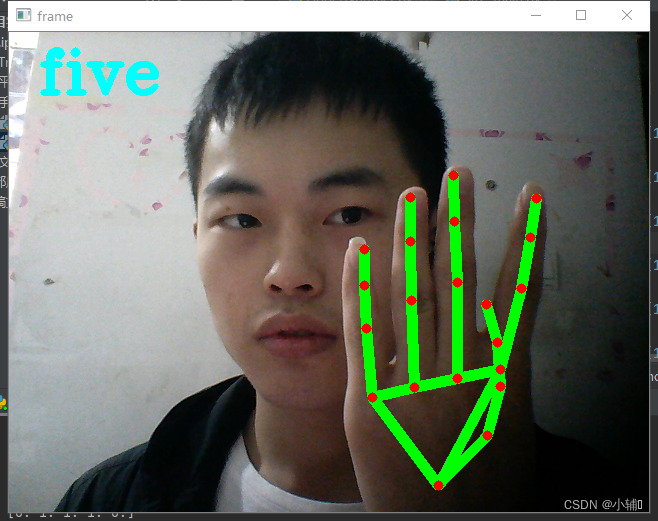
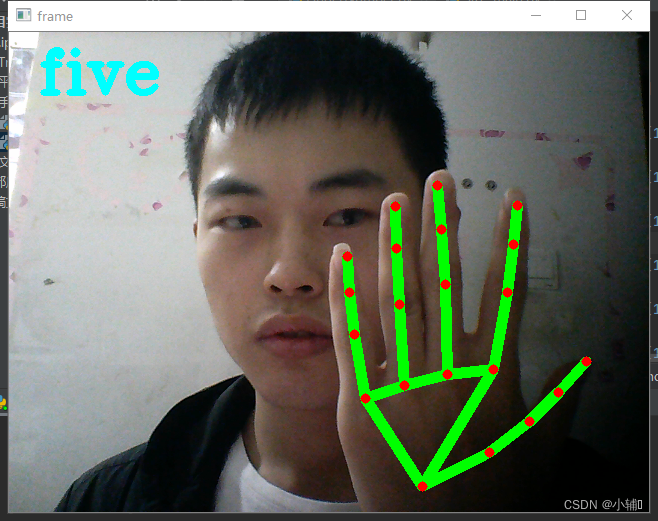
gesture = "five"
elif (result[0] == 1) and (result[1] == 0) and (result[2] == 0) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 1):
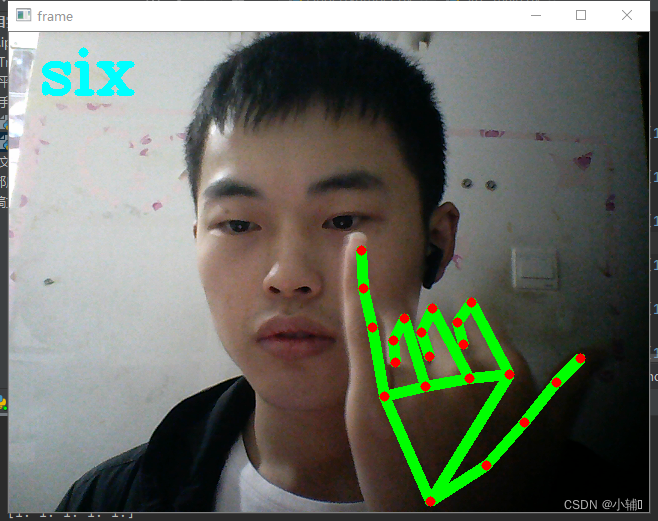
gesture = "six"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 0) and (result[2] == 1) and (result[3] == 1) and (result[4] == 1):
gesture = "OK"
elif (result[0] == 0) and (result[1] == 0) and (result[2] == 0) and (result[3] == 0) and (result[4] == 0):
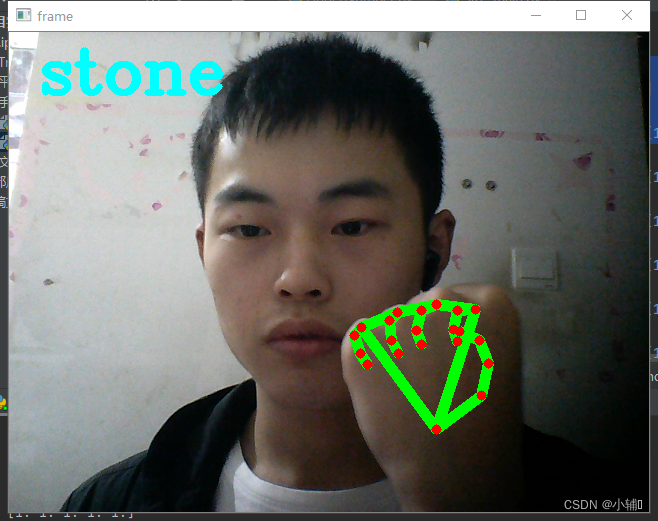
gesture = "stone"
else:
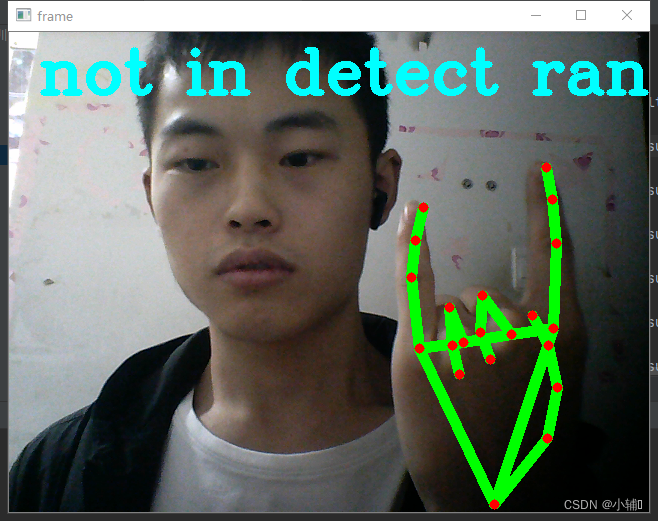
gesture = "not in detect range..."
return gesture
三.函数调用与机器视觉判断
def detect():
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
# 加载手部检测函数
mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mpHands.Hands()
# 加载绘制函数,并设置手部关键点和连接线的形状、颜色
mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
handLmsStyle = mpDraw.DrawingSpec(color=(0, 0, 255), thickness=int(5))
handConStyle = mpDraw.DrawingSpec(color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=int(10))
figure = np.zeros(5)
landmark = np.empty((21, 2))
if not cap.isOpened():
print("Can not open camera.")
exit()
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("Can not receive frame. Exiting...")
break
frame_RGB = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
result = hands.process(frame_RGB)
# 读取视频图像的高和宽
frame_height = frame.shape[0]
frame_width = frame.shape[1]
# print(result.multi_hand_landmarks)
# 如果检测到手
if result.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 为每个手绘制关键点和连接线
for i, handLms in enumerate(result.multi_hand_landmarks):
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(frame,
handLms,
mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
landmark_drawing_spec=handLmsStyle,
connection_drawing_spec=handConStyle)
for j, lm in enumerate(handLms.landmark):
xPos = int(lm.x * frame_width)
yPos = int(lm.y * frame_height)
landmark_ = [xPos, yPos]
landmark[j, :] = landmark_
# 通过判断手指尖与手指根部到0位置点的距离判断手指是否伸开(拇指检测到17点的距离)
for k in range(5):
if k == 0:
figure_ = finger_stretch_detect(landmark[17], landmark[4 * k + 2], landmark[4 * k + 4])
else:
figure_ = finger_stretch_detect(landmark[0], landmark[4 * k + 2], landmark[4 * k + 4])
figure[k] = figure_
print(figure, '\n')
gesture_result = detect_hands_gesture(figure)
cv.putText(frame, f"{gesture_result}", (30, 60 * (i + 1)), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 2, (255, 255, 0), 5)
cv.imshow('frame', frame)
if cv.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
detect()结果展示:
定义了one-six数字,以及石头,未定义
(根据你手指弯曲状态判定为0或1,再判定手势代表的意义)
总结
全部代码都放在这了,有需要的小伙伴直接复制就可以了
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)