C++11 的 运行时类型识别type_info
一、type_info与typeid类type_info保存关于类型的特定于实现的信息,包括类型的名称,以及比较两个类型是否相等或排序顺序的方法。 这是typeid操作符返回的类。具有如下特点:(1)这个类的构造函数是private的,因此用户不能直接构造这样的对象,只能通过typeid()函数来获取这个对象.(2)这个类对外提供了name(),operator==()等方法供用户使用.(3)ty
一、type_info与typeid
类type_info保存关于类型的特定于实现的信息,包括类型的名称,以及比较两个类型是否相等或排序顺序的方法。 这是typeid操作符返回的类。具有如下特点:
(1)这个类的构造函数是private的,因此用户不能直接构造这样的对象,只能通过typeid()函数来获取这个对象.
(2)这个类对外提供了name(),operator==()等方法供用户使用.
(3)typeid()可以对基本的数据类型和对象进行操作,这种情况下,是在编译期静态决定的.
(4)type_info也可以对类类型和类对象进行操作,分两种情况:如果是声明了虚函数的类对象引用,则typeid()返回的是实际对象的类型信息,在运行时动态决定的;反之(没有定义虚函数,或者即使定义了虚函数但传入的是对象指针),则typeid()返回的是入参声明类型信息,在编译时静态决定的.
// type_index example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <typeinfo> // operator typeid
#include <typeindex> // std::type_index
#include <string>
int main()
{
char a = 'a';
short b = 10;
int c = 99;
long d = 20;
float e = 2.3;
double f = 4.8;
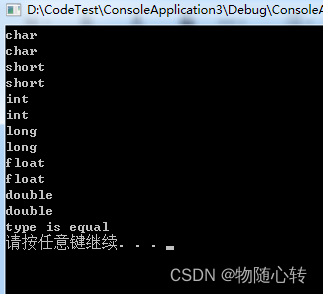
cout << typeid(char).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(a).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(short).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(b).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(int).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(long).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(d).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(float).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(e).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(double).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(f).name() << endl;
if (typeid(f) == typeid(double)) {
cout << "type is equal" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "type is not equal" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
打印
二、type_index
type_index类在头文件<typeindex>中声明,它是type_info对象的一个封装类,可以用作关联容器(比如map)和无序关联容器(比如unordered_map)的索引。
// type_index example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <typeinfo> // operator typeid
#include <typeindex> // std::type_index
#include <unordered_map> // std::unordered_map
#include <string>
typedef struct C {};
int main()
{
std::unordered_map<std::type_index, std::string> mytypes;
mytypes[typeid(int)] = "Integer type";
mytypes[typeid(double)] = "Floating-point type";
mytypes[typeid(C)] = "Custom class named C";
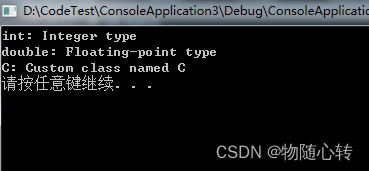
std::cout << "int: " << mytypes[typeid(int)] << '\n';
std::cout << "double: " << mytypes[typeid(double)] << '\n';
std::cout << "C: " << mytypes[typeid(C)] << '\n';
system("pause");
return 0;
}
打印
参考:
std::type_info - cppreference.com
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)