Pytorch深度学习案例6:VGG-16实现人脸识别
VGG-16(Visual Geometry Group-16)是由牛津大学视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)提出的一种深度卷积神经网络架构,用于图像分类和对象识别任务。VGG-16在2014年被提出,是VGG系列中的一种。VGG-16之所以备受关注,是因为它在ImageNet图像识别竞赛中取得了很好的成绩,展示了其在大规模图像识别任务中的有效性。此数据集的结构为:face文
·
一 前期准备
1.设置GPU/CPU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
devicedevice(type='cpu')
2.导入数据
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
data_dir = './face/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[1] for path in data_paths]
classeNames['Angelina Jolie', 'Brad Pitt', 'Denzel Washington', 'Hugh Jackman', 'Jennifer Lawrence', 'Johnny Depp', 'Kate Winslet', 'Leonardo DiCaprio', 'Megan Fox', 'Natalie Portman', 'Nicole Kidman', 'Robert Downey Jr', 'Sandra Bullock', 'Scarlett Johansson', 'Tom Cruise', 'Tom Hanks', 'Will Smith']
此数据集的结构为:face文件夹下有一些分类文件夹,每个子文件夹都对应一个人进行识别分类。
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("./face/",transform=train_transforms)
total_dataDataset ImageFolder
Number of datapoints: 1800
Root location: ./face/
StandardTransform
Transform: Compose(
Resize(size=[224, 224], interpolation=bilinear, max_size=None, antialias=warn)
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
)
total_data.class_to_idx # 数值化分类{'Angelina Jolie': 0,
'Brad Pitt': 1,
'Denzel Washington': 2,
'Hugh Jackman': 3,
'Jennifer Lawrence': 4,
'Johnny Depp': 5,
'Kate Winslet': 6,
'Leonardo DiCaprio': 7,
'Megan Fox': 8,
'Natalie Portman': 9,
'Nicole Kidman': 10,
'Robert Downey Jr': 11,
'Sandra Bullock': 12,
'Scarlett Johansson': 13,
'Tom Cruise': 14,
'Tom Hanks': 15,
'Will Smith': 16}
3.划分训练集
# 划分训练集
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
train_dataset, test_dataset
batch_size = 32
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
for X, y in test_dl:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
breakShape of X [N, C, H, W]: torch.Size([32, 3, 224, 224]) Shape of y: torch.Size([32]) torch.int64
4.数据可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
# 指定图像文件夹路径
image_folder = './face/Megan Fox/'
# 获取文件夹中的所有图像文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith((".jpg", ".png", ".jpeg"))]
# 创建Matplotlib图像
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 8, figsize=(16, 6))
# 使用列表推导式加载和显示图像
for ax, img_file in zip(axes.flat, image_files):
img_path = os.path.join(image_folder, img_file)
img = Image.open(img_path)
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
# 显示图像
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
二 调用官方的VGG-16模型
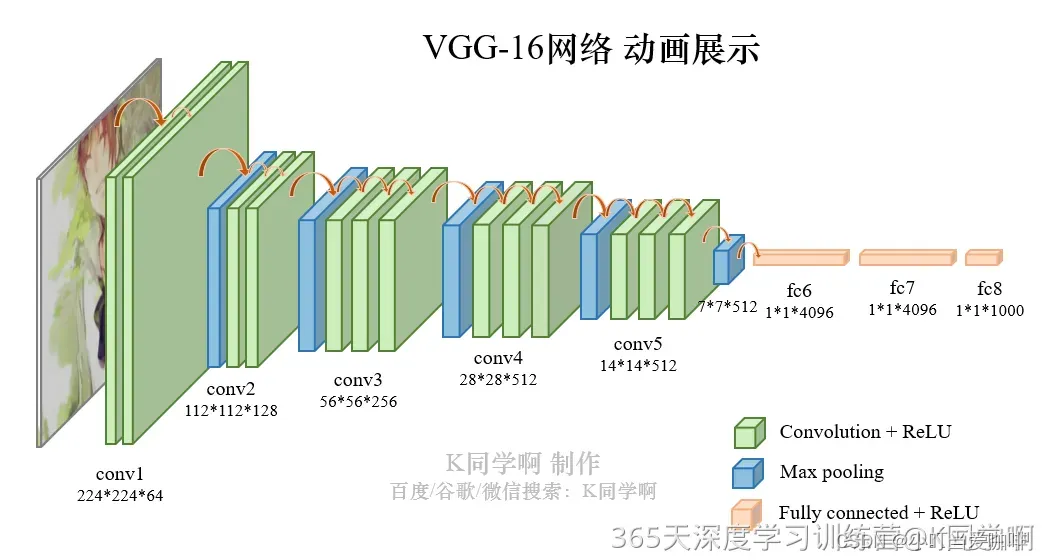
VGG-16(Visual Geometry Group-16)是由牛津大学视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)提出的一种深度卷积神经网络架构,用于图像分类和对象识别任务。VGG-16在2014年被提出,是VGG系列中的一种。VGG-16之所以备受关注,是因为它在ImageNet图像识别竞赛中取得了很好的成绩,展示了其在大规模图像识别任务中的有效性。
以下是VGG-16的主要特点:
- 深度:VGG-16由16个卷积层和3个全连接层组成,因此具有相对较深的网络结构。这种深度有助于网络学习到更加抽象和复杂的特征。
- 卷积层的设计:VGG-16的卷积层全部采用
3x3的卷积核和步长为1的卷积操作,同时在卷积层之后都接有ReLU激活函数。这种设计的好处在于,通过堆叠多个较小的卷积核,可以提高网络的非线性建模能力,同时减少了参数数量,从而降低了过拟合的风险。- 池化层:在卷积层之后,VGG-16使用最大池化层来减少特征图的空间尺寸,帮助提取更加显著的特征并减少计算量。
- 全连接层:VGG-16在卷积层之后接有3个全连接层,最后一个全连接层输出与类别数相对应的向量,用于进行分类。
VGG-16结构说明:
- 13个卷积层(Convolutional Layer),分别用
blockX_convX表示;- 3个全连接层(Fully connected Layer),用
classifier表示;- 5个池化层(Pool layer)。
VGG-16包含了16个隐藏层(13个卷积层和3个全连接层),故称为VGG-16
from torchvision.models import vgg16
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
# 加载预训练模型,并且对模型进行微调
model = vgg16(pretrained = True).to(device) # 加载预训练的vgg16模型
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False # 冻结模型的参数,这样子在训练的时候只训练最后一层的参数
# 修改classifier模块的第6层(即:(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2, bias=True))
# 注意查看我们下方打印出来的模型
model.classifier._modules['6'] = nn.Linear(4096,len(classeNames)) # 修改vgg16模型中最后一层全连接层,输出目标类别个数
model.to(device)
modelUsing cpu device
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(17): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(18): ReLU(inplace=True)
(19): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(24): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(25): ReLU(inplace=True)
(26): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(27): ReLU(inplace=True)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(7, 7))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=17, bias=True)
)
)
三 训练模型
1.编写训练函数
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss2.编写测试函数
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss3.正式训练
learn_rate = 1e-4 # 初始学习率
# 调用官方动态学习率接口时使用
lambda1 = lambda epoch: 0.92 ** (epoch // 4)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda1) #选定调整方法import copy
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
epochs = 40
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
best_acc = 0 # 设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 更新学习率(使用自定义学习率时使用)
# adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, learn_rate)
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
scheduler.step() # 更新学习率(调用官方动态学习率接口时使用)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
# 保存最佳模型到 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
PATH = './best_model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
print('Done')Epoch: 1, Train_acc:6.8%, Train_loss:2.875, Test_acc:7.2%, Test_loss:2.810, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 2, Train_acc:7.7%, Train_loss:2.858, Test_acc:10.0%, Test_loss:2.775, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 3, Train_acc:9.2%, Train_loss:2.817, Test_acc:12.2%, Test_loss:2.757, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 4, Train_acc:11.0%, Train_loss:2.794, Test_acc:14.4%, Test_loss:2.736, Lr:9.20E-05 Epoch: 5, Train_acc:12.2%, Train_loss:2.775, Test_acc:15.3%, Test_loss:2.710, Lr:9.20E-05 Epoch: 6, Train_acc:13.9%, Train_loss:2.730, Test_acc:16.7%, Test_loss:2.704, Lr:9.20E-05 Epoch: 7, Train_acc:13.4%, Train_loss:2.744, Test_acc:16.9%, Test_loss:2.681, Lr:9.20E-05 Epoch: 8, Train_acc:14.2%, Train_loss:2.715, Test_acc:16.7%, Test_loss:2.659, Lr:8.46E-05 Epoch: 9, Train_acc:15.2%, Train_loss:2.710, Test_acc:16.7%, Test_loss:2.651, Lr:8.46E-05 Epoch:10, Train_acc:14.0%, Train_loss:2.664, Test_acc:17.5%, Test_loss:2.627, Lr:8.46E-05 Epoch:11, Train_acc:16.1%, Train_loss:2.659, Test_acc:16.9%, Test_loss:2.618, Lr:8.46E-05 Epoch:12, Train_acc:16.4%, Train_loss:2.644, Test_acc:17.5%, Test_loss:2.620, Lr:7.79E-05 Epoch:13, Train_acc:15.8%, Train_loss:2.651, Test_acc:17.5%, Test_loss:2.598, Lr:7.79E-05 Epoch:14, Train_acc:17.6%, Train_loss:2.609, Test_acc:17.5%, Test_loss:2.592, Lr:7.79E-05 Epoch:15, Train_acc:16.0%, Train_loss:2.609, Test_acc:17.8%, Test_loss:2.572, Lr:7.79E-05 Epoch:16, Train_acc:16.3%, Train_loss:2.582, Test_acc:17.5%, Test_loss:2.557, Lr:7.16E-05 Epoch:17, Train_acc:18.8%, Train_loss:2.577, Test_acc:18.1%, Test_loss:2.568, Lr:7.16E-05 Epoch:18, Train_acc:17.9%, Train_loss:2.560, Test_acc:18.1%, Test_loss:2.560, Lr:7.16E-05 Epoch:19, Train_acc:16.2%, Train_loss:2.570, Test_acc:18.1%, Test_loss:2.548, Lr:7.16E-05 Epoch:20, Train_acc:18.8%, Train_loss:2.560, Test_acc:18.1%, Test_loss:2.536, Lr:6.59E-05 Epoch:21, Train_acc:18.9%, Train_loss:2.533, Test_acc:18.3%, Test_loss:2.527, Lr:6.59E-05 Epoch:22, Train_acc:17.4%, Train_loss:2.539, Test_acc:18.9%, Test_loss:2.522, Lr:6.59E-05 Epoch:23, Train_acc:18.1%, Train_loss:2.518, Test_acc:18.6%, Test_loss:2.509, Lr:6.59E-05 Epoch:24, Train_acc:18.1%, Train_loss:2.503, Test_acc:18.6%, Test_loss:2.530, Lr:6.06E-05 Epoch:25, Train_acc:20.1%, Train_loss:2.509, Test_acc:18.6%, Test_loss:2.516, Lr:6.06E-05 Epoch:26, Train_acc:19.4%, Train_loss:2.505, Test_acc:18.6%, Test_loss:2.490, Lr:6.06E-05 Epoch:27, Train_acc:19.8%, Train_loss:2.492, Test_acc:18.9%, Test_loss:2.484, Lr:6.06E-05 Epoch:28, Train_acc:19.7%, Train_loss:2.483, Test_acc:18.9%, Test_loss:2.477, Lr:5.58E-05 Epoch:29, Train_acc:20.3%, Train_loss:2.476, Test_acc:19.2%, Test_loss:2.484, Lr:5.58E-05 Epoch:30, Train_acc:19.0%, Train_loss:2.486, Test_acc:19.4%, Test_loss:2.480, Lr:5.58E-05 Epoch:31, Train_acc:20.8%, Train_loss:2.461, Test_acc:20.0%, Test_loss:2.469, Lr:5.58E-05 Epoch:32, Train_acc:18.5%, Train_loss:2.480, Test_acc:20.3%, Test_loss:2.464, Lr:5.13E-05 Epoch:33, Train_acc:20.6%, Train_loss:2.461, Test_acc:20.3%, Test_loss:2.467, Lr:5.13E-05 Epoch:34, Train_acc:20.8%, Train_loss:2.462, Test_acc:20.6%, Test_loss:2.450, Lr:5.13E-05 Epoch:35, Train_acc:19.9%, Train_loss:2.445, Test_acc:20.8%, Test_loss:2.450, Lr:5.13E-05 Epoch:36, Train_acc:18.7%, Train_loss:2.448, Test_acc:20.8%, Test_loss:2.444, Lr:4.72E-05 Epoch:37, Train_acc:19.3%, Train_loss:2.445, Test_acc:21.4%, Test_loss:2.445, Lr:4.72E-05 Epoch:38, Train_acc:22.2%, Train_loss:2.425, Test_acc:21.4%, Test_loss:2.437, Lr:4.72E-05 Epoch:39, Train_acc:20.6%, Train_loss:2.440, Test_acc:21.4%, Test_loss:2.440, Lr:4.72E-05 Epoch:40, Train_acc:20.8%, Train_loss:2.427, Test_acc:21.4%, Test_loss:2.438, Lr:4.34E-05 Done
四 结果可视化
1.loss和Accuary图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 #分辨率
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show() 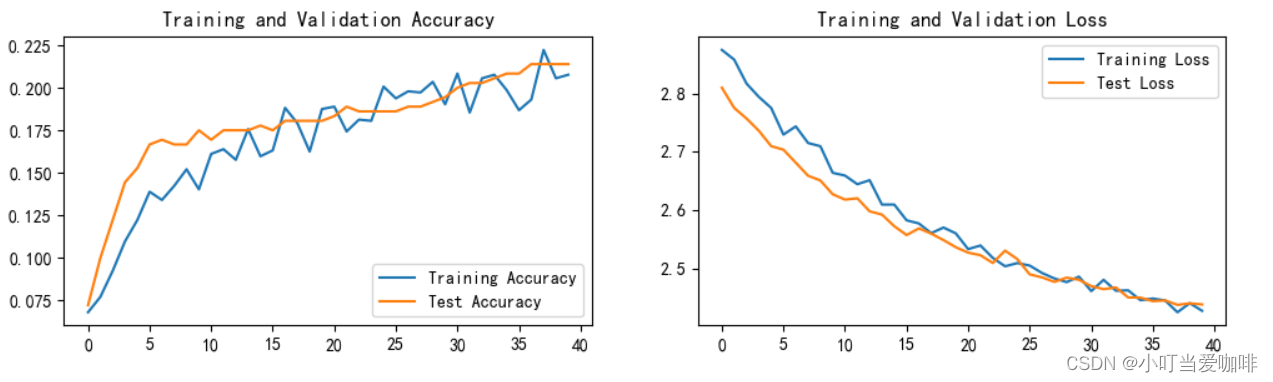
2.指定图片进行预测
from PIL import Image
classes = list(total_data.class_to_idx)
def predict_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_img = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
plt.imshow(test_img) # 展示预测的图片
test_img = transform(test_img)
img = test_img.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(img)
_,pred = torch.max(output,1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print(f'预测结果是:{pred_class}')
# 预测训练集中的某张照片
predict_one_image(image_path='./face/Kate Winslet/005_93b2fce9.jpg',
model=model,
transform=train_transforms,
classes=classes) 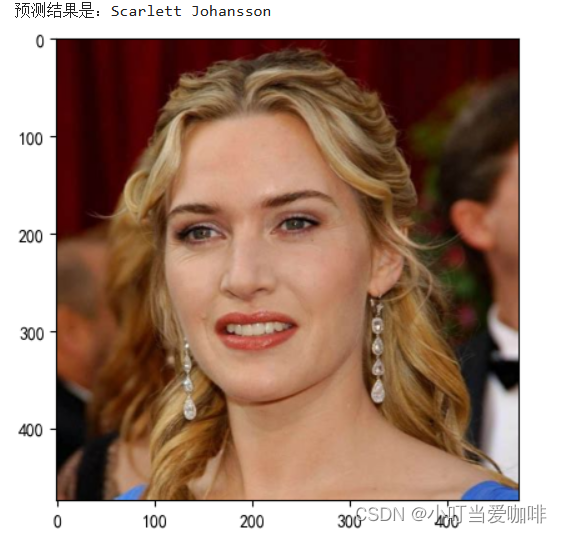
五 模型评估
best_model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, best_model, loss_fn)
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss(0.21388888888888888, 2.432936449845632)
# 查看是否与我们记录的最高准确率一致
epoch_test_acc0.21388888888888888
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12条内容
已为社区贡献12条内容







所有评论(0)