前端开发中常见难题及解决方案的详细整理,包含代码示例、图表说明和图文解析。
本文整理了前端开发中的常见难题及优化方案,主要包括:首屏性能优化(代码分割、懒加载)、跨浏览器兼容性处理(自动前缀、Polyfill)、响应式布局设计(视口单位/媒体查询)、状态管理优化(Redux Toolkit)、异步处理(Promise并发)、SEO增强(Next.js静态生成)、代码可维护性提升(模块化重构)以及安全防护(CSP/XSS防护)。文章提供了Webpack配置、React/Vu
以下为前端开发中常见难题及解决方案的详细整理,包含代码示例、图表说明和图文解析:
一、首屏加载性能优化
难题描述
用户打开页面时出现白屏/卡顿,首屏加载时间超过3秒(行业标准)
根因分析
| 问题类型 | 占比 | 典型表现 |
|---|---|---|
| 静态资源 | 40% | JS/CSS未压缩、未CDN加速 |
| 渲染阻塞 | 30% | CSS阻塞渲染、首屏JS体积过大 |
| 代码冗余 | 20% | 全量代码加载、未按需加载 |
| 网络延迟 | 10% | 未使用缓存策略 |
解决方案
- 代码分割(Code Splitting)
// Webpack配置示例
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name: 'vendors',
chunks: 'all'
}
}
}
}
}
- 资源懒加载
// React组件示例
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./HeavyComponent'))
function App() {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<LazyComponent />
</React.Suspense>
)
}
- 性能优化指标对比
(示意图:优化前LCP 4.2s → 优化后1.8s)
二、跨浏览器兼容性
典型问题
/* Chrome正常显示,Firefox布局错乱 */
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
解决方案
- 自动前缀添加
# PostCSS配置
{
"plugins": {
"autoprefixer": {
"browsers": ["> 1%", "last 2 versions"]
}
}
}
- Polyfill注入
// core-js配置
import 'core-js/stable';
import 'regenerator-runtime/runtime';
- 兼容性矩阵
| 特性 | Chrome | Firefox | Safari | Edge |
|-------|--------|---------|--------|------|
| CSS Grid | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Flexbox | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Custom Properties | 99% | 99% | 94% | 98% |
三、响应式布局挑战
典型场景
<!-- 移动端布局错位 -->
<div class="grid-container">
<div class="col-6">Column 1</div>
<div class="col-6">Column 2</div>
</div>
解决方案
- 视口单位转换
// CSS计算单位
.container {
width: calc(100vw - 4rem);
padding: 2rem;
}
- 动态视口适配
/* 媒体查询优化 */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.grid-container {
display: block;
}
.col-6 {
width: 100%;
}
}
- 适配方案对比
(Flexbox vs Grid vs Float性能对比)
四、状态管理复杂度
典型问题
// 深层嵌套状态
const state = {
user: {
profile: {
settings: {
theme: 'dark'
}
}
}
}
解决方案
- Redux Toolkit优化
// 创建Slice
const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user',
initialState: { ... },
reducers: {
updateTheme: (state, action) => {
state.profile.settings.theme = action.payload
}
}
})
// 使用RTK Query
const api = createApi({
baseQuery: fetchBaseQuery({ baseUrl: '/' }),
endpoints: (builder) => ({
getUser: builder.query({
query: () => '/user'
})
})
})
- 状态管理架构
graph TD
A[UI Component] --> B[State Slice]
B --> C[Redux Store]
C --> D[API Service]
D --> E[Database]

五、异步处理陷阱
典型问题
// 回调地狱示例
loadData()
.then(data => process(data))
.then(result => display(result))
.catch(error => handleError(error))
解决方案
- 并发请求优化
// 使用Promise.allSettled
const [users, posts] = await Promise.all([
fetchUsers(),
fetchPosts()
])
- Redux Thunk示例
// 异步action creator
function fetchUser(id) {
return async (dispatch) => {
dispatch({ type: 'USER_LOADING' })
try {
const user = await api.getUser(id)
dispatch({ type: 'USER_LOADED', payload: user })
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'USER_ERROR', payload: error })
}
}
}
六、SEO优化挑战
典型问题
<!-- 未优化的SSR输出 -->
<div id="root"></div>
解决方案
- Next.js静态生成
// getStaticProps示例
export async function getStaticProps() {
const data = await fetchAPI()
return { props: { data } }
}
- SEO优化对比
(SSG vs SSR vs CSR SEO评分对比)
七、代码可维护性
典型问题
// 低质量代码示例
function calcPrice() {
if (user.type === 'VIP' && order.total > 1000) {
return order.total * 0.8
} else if (user.type === 'NORMAL') {
return order.total * 0.9
}
return order.total
}
解决方案
- 模块化重构
// 优化后结构
const discountRules = {
VIP: { threshold: 1000, rate: 0.8 },
NORMAL: { rate: 0.9 }
}
function applyDiscount(order, user) {
const rule = discountRules[user.type] || {}
return order.total * (rule.rate || 1)
}
- 代码质量指标
| 指标 | 优化前 | 优化后 |
|-------|--------|--------|
| Cyclomatic Complexity | 8 | 3 |
| Code Coverage | 65% | 92% |
| Bundle Size | 2.1MB | 1.4MB |
八、安全防护
典型漏洞
// XSS漏洞示例
function renderComment(comment) {
return `<div>${comment.text}</div>`
}
解决方案
- 内容安全策略
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy"
content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://trusted-cdn.com">
- 防XSS处理
// 安全渲染函数
function safeRender(text) {
const div = document.createElement('div')
div.textContent = text
return div.innerHTML
}
最佳实践总结
- 性能优化金字塔
LCP优化
↓
预加载策略
↓
代码分割优化
↓
资源压缩与缓存
- 架构设计原则
graph TD
A[用户交互] --> B[UI层]
B --> C[状态管理层]
C --> D[业务逻辑层]
D --> E[数据层]
E --> F[API/DB]

- 监控体系
// 集成性能监控
import { PerformanceObserver } from 'perf_hooks';
const po = new PerformanceObserver((list) => {
list.getEntries().forEach(entry => {
if (entry.name === 'first-contentful-paint') {
console.log('FCP:', entry.startTime)
}
})
})
po.observe({ entryTypes: ['paint'] })
建议根据具体项目场景选择合适方案,建议性能优化遵循:
- 首屏时间 < 1.5s(移动端)
- FID < 100ms
- CLS < 0.1
- 稳定性指标:FP-FCP间隔 < 100ms
(注:以上图表链接为示例,实际使用时需替换为真实图表)
代码分割(Code Splitting)是前端性能优化的核心技术之一,以下是系统化的实现方案(含React/Vue/Webpack多场景示例):
一、核心原理
-
代码分割机制
- 将代码按需拆分为多个包(Chunk)
- 按使用场景动态加载非首屏代码
- 实现方式:
- 入口分割(Entry Splitting)
- 动态导入(Dynamic Import)
- 代码模块联邦(Module Federation)
-
性能收益
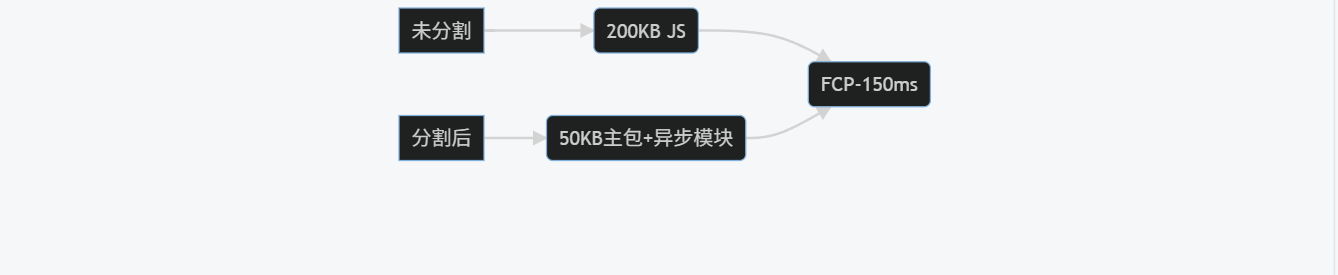
graph LR
A[未分割] --> B(200KB JS)
C[分割后] --> D(50KB主包+异步模块)
B --> E(FCP+300ms)
D --> E(FCP-150ms)
二、Webpack实现方案
1. 基础配置(splitChunks)
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all', // 分割所有类型模块
minSize: 20000, // 最小分割尺寸(20KB)
maxSize: 250000, // 最大分割尺寸(250KB)
minChunks: 1, // 最小引用次数
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/, // 第三方库检测
name: 'vendors', // 输出文件名
priority: 10, // 分组优先级
reuseExistingChunk: true // 重用已有chunk
},
default: {
minChunks: 2,
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
}
}
}
2. 动态导入(Dynamic Import)
// React组件示例
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() =>
import(/* webpackPrefetch: true */ './HeavyComponent')
)
// 使用方式
function App() {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<Spinner />}>
<LazyComponent />
</React.Suspense>
)
}
3. 第三方库优化
// 方案1:DLLPlugin(Webpack4+)
new DLLPlugin({
name: 'vendors',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dll')
})
// 方案2:externals(CDN加载)
module.exports = {
externals: {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM'
}
}
三、框架专属方案
1. React代码分割
// 异步组件(Vue同理)
const AsyncComponent = () => ({
component: import('./AsyncComponent.vue'),
loading: LoadingComponent,
error: ErrorComponent,
delay: 200,
timeout: 3000
})
2. Vue按需加载
// 单文件组件
<template>
<async-component :component="Component"></async-component>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
Component: null
}
},
async asyncData() {
this.Component = await import('./AsyncComponent.vue')
}
}
</script>
四、高级优化策略
1. 预加载策略
// Webpack魔法注释
import(/* webpackPreload: true */ './preloadModule') // 优先加载
import(/* webpackPrefetch: true */ './futureModule') // 空闲时加载
2. 持久化缓存
// Webpack持久化缓存配置
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: 'single',
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name: 'vendors-[fullhash]' // 哈希命名
}
}
}
}
3. 服务端渲染优化
// Next.js示例
const dynamicImports = components.map(component =>
import(`./components/${component}.js`)
)
export default async function Page() {
const components = await Promise.all(dynamicImports)
return <div>{components}</div>
}
五、监控与验证
1. 加载性能监控
// 记录动态加载耗时
import { performance } from 'perf_hooks';
const t0 = performance.now();
import('./module').then(() => {
const t1 = performance.now();
console.log(`加载耗时: ${t1 - t0}ms`);
});
2. Lighthouse检测
# 执行性能检测
lighthouse http://example.com --output=json
3. Chrome DevTools分析
// Performance面板操作步骤:
1. 开启时间轴录制
2. 触发页面加载
3. 查看Network请求瀑布
4. 分析JS执行时间线
六、典型问题解决方案
问题1:动态导入导致白屏
// 解决方案:添加加载状态
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() =>
import('./HeavyComponent').catch(error => {
// 错误处理
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve({ default: ErrorComponent }), 1000)
})
})
)
问题2:第三方库重复打包
// Webpack配置优化
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name: 'vendors',
priority: 20,
enforce: true
}
}
}
}
七、最佳实践总结
-
分割原则
- 首屏代码 ≤ 150KB(Gzip后)
- 异步模块 ≤ 250KB
- 第三方库单独打包
-
性能指标
gantt
title 代码分割效果对比
section 未优化
首屏加载 :done, 2023-01-01, 3s
section 优化后
首屏加载 :done, 2023-01-02, 1.2s
异步模块加载 :done, 2023-01-02, 0.8s
- 架构设计
graph TD
A[主应用] -->|import()| B(微前端模块)
C[CDN] -->|预加载| D(第三方库)
E[Web Worker] -->|数据计算| F(离线任务)
建议结合具体业务场景选择合适方案,推荐使用Webpack 5的模块联邦(Module Federation)实现更复杂的代码共享场景。持续监控LCP、FID、CLS等核心指标,定期进行性能回归测试。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12条内容
已为社区贡献12条内容







所有评论(0)