Java设计模式-13、外观模式-统一的入口
第13章:外观模式-统一的入口定义:外观模式:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个统一的入口。外观模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。迪米特法则的一种具体实现(一个对象应该对其他对象保持最少的了解)又称:门面模式结构:代码实现://子系统class SubSystemA {public void MethodA() {//业务实现代码}}class SubSystemB {publ
·
第13章:外观模式-统一的入口
定义:
外观模式:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个统一的入口。外观模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
迪米特法则的一种具体实现(一个对象应该对其他对象保持最少的了解)
又称:门面模式


结构:

代码实现:
//子系统
class SubSystemA {
public void MethodA() {
//业务实现代码
}
}
class SubSystemB {
public void MethodB() {
//业务实现代码
}
}
class SubSystemC {
public void MethodC() {
//业务实现代码
}
}
//外观类
class Facade {
private SubSystemA obj1 = new SubSystemA();
private SubSystemB obj2 = new SubSystemB();
private SubSystemC obj3 = new SubSystemC();
public void Method() {
obj1.MethodA();
obj2.MethodB();
obj3.MethodC();
}
}
//客户端
class Program {
static void Main(String[] args) {
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.Method();
}
}
应用实例:
文件加密模块:
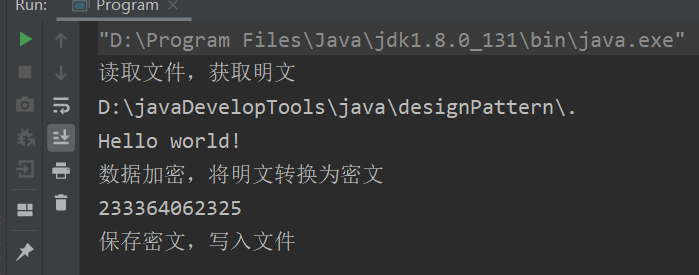
- 读取源文件:使用流
- 加密:求模
- 保存加密文件:使用流

//文件读取
class FileReader{
public String reade(String fileNameSrc){
System.out.println("读取文件,获取明文");
FileInputStream fs=null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
System.out.println(new File(".").getAbsolutePath()); //打印绝对路径
fs=new FileInputStream("demo\\src\\"+fileNameSrc);
int data;
while ((data=fs.read())!=-1){
sb=sb.append((char)data);
}
fs.close();
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("文件不存在或文件错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
//数据加密类,充当子系统类
class CipherMachine{
public String encrypt(String plainText){
System.out.println("数据加密,将明文转换为密文");
String es="";
char[] chars = plainText.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chars) {
String c=String.valueOf((ch%7));
es+=c;
}
System.out.println(es);
return es;
}
}
//文件保存类,充当子系统
class FileWriter{
public void write(String encryptStr,String fileNameDes){
System.out.println("保存密文,写入文件");
FileOutputStream fs=null;
try {
fs=new FileOutputStream("demo\\src\\"+fileNameDes);
byte[] str=encryptStr.getBytes();
fs.write(str,0,str.length);
fs.flush();
fs.close();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("文件不存在或文件操作错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//加密外观类,充当外观类
class EncryptFacade{
private FileReader reader;
private CipherMachine cipher;
private FileWriter writer;
public EncryptFacade(){
reader=new FileReader();
cipher=new CipherMachine();
writer=new FileWriter();
}
public void fileEncrypt(String fileNameScr,String fileNameDes){
String plainStr = reader.reade(fileNameScr);
String encryptStr = cipher.encrypt(plainStr);
writer.write(encryptStr,fileNameDes);
}
}
//主程序
class Program{
public static void main(String[] args) {
EncryptFacade ef = new EncryptFacade();
ef.fileEncrypt("src.txt","des.txt");
}
}
抽象外观类
当需要增加、删除或更换与外观类交互的子系统时,可使用抽象外观类
使用新的加密方式,需要引入抽象外管理类才能遵守开闭原则
//新的加密类
class NewCipherMachine {
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
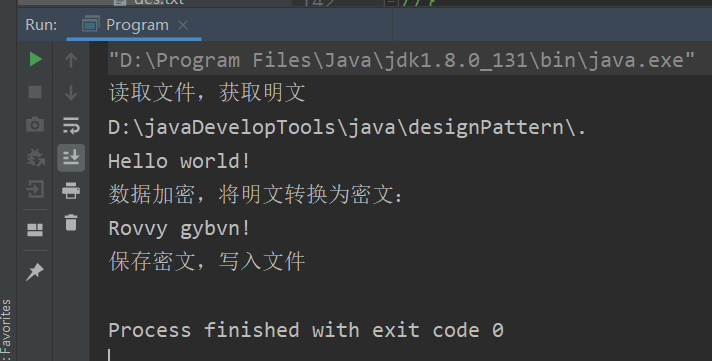
System.out.println("数据加密,将明文转换为密文:");
String es = "";
int key = 10;//设置密钥,移位数为10
char[] chars = plainText.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chars) {
int temp = ch;
//小写字母移位
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
temp += key % 26;
if (temp > 122) temp -= 26;
if (temp < 97) temp += 26;
}
//大写字母移位
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
temp += key % 26;
if (temp > 90) temp -= 26;
if (temp < 65) temp += 26;
}
es += String.valueOf((char)temp);
}
System.out.println(es);
return es;
}
}
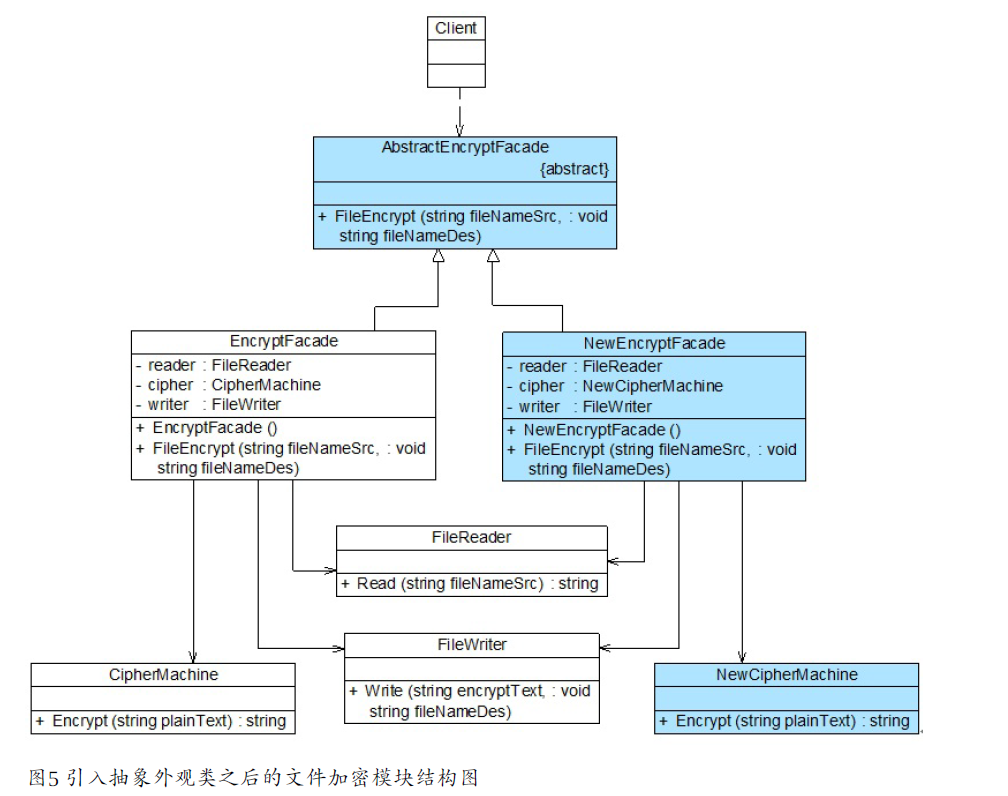
//抽象外观类
abstract class AbstractEncryptFacade {
public abstract void FileEncrypt(String fileNameSrc, String fileNameDes);
}
//新的加密外观类
class NewEncryptFacade extends AbstractEncryptFacade {
private FileReader reader;
private NewCipherMachine cipher;
private FileWriter writer;
public NewEncryptFacade() {
reader = new FileReader();
cipher = new NewCipherMachine();
writer = new FileWriter();
}
@Override
public void FileEncrypt(String fileNameSrc, String fileNameDes) {
String plainStr = reader.reade(fileNameSrc);
String encryptStr = cipher.encrypt(plainStr);
writer.write(encryptStr, fileNameDes);
}
}
class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractEncryptFacade ef = new NewEncryptFacade(); //针对抽象外观类编程
ef.FileEncrypt("src.txt", "des.txt");
}
}
主程序中可使用xml配置文件和反射实现外观类对象
优点:
- 它对客户端屏蔽了子系统组件,减少了客户端所需处理的对象数目,并使得子系统使用起来更加容易。通过引入外观模式,客户端代码将变得很简单,与之关联的对象也很少。
- 它实现了子系统与客户端之间的松耦合关系,这使得子系统的变化不会影响到调用它的客户端,只需要调整外观类即可。
- 一个子系统的修改对其他子系统没有任何影响,而且子系统内部变化也不会影响到外观对象。
缺点:
- 不能很好地限制客户端直接使用子系统类,如果对客户端访问子系统类做太多的限制则减少了可变性和灵活 性。
- 如果设计不当,增加新的子系统可能需要修改外观类的源代码,违背了开闭原则。
适用场景:
- 当要为访问一系列复杂的子系统提供一个简单入口时可以使用外观模式。
- 客户端程序与多个子系统之间存在很大的依赖性。引入外观类可以将子系统与客户端解耦,从而提高子系统的独立性和可移植性。
- 在层次化结构中,可以使用外观模式定义系统中每一层的入口,层与层之间不直接产生联系,而通过外观类建立联系,降低层之间的耦合度。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)