深度学习与自然语言处理作业第一次作业——中文平均信息熵计算
深度学习与自然语言处理作业第一次作业————中文平均信息熵计算
深度学习与自然语言处理作业
第一次作业————中文平均信息熵计算
文章目录
一、文章背景
首先阅读课程提供的英文文章,参考文章来计算所提供数据库中文的平均信息熵。
二、实验原理
1、信息熵
根据论文,对于文本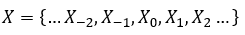
来说,它的信息熵定义为: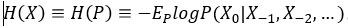
其中信息熵具有三个基本性质:
1、单调性,发生概率越高的事件,其携带的信息量越低;
2、非负性,信息熵可以看作为一种广度量,非负性是一种合理的必然;
3、累加性,即多随机事件同时发生存在的总不确定性的量度是可以表示为各事件不确定性的量度的和,这也是广度量的一种体现。
2、N_Gram 语言模型
根据大数定理,当统计量足够大的时候,词、二元词组、三元词组出现的概率大致等于其出现的频率。
则有一元模型的信息熵计算公式为: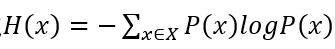
其中P(x)可近似于每个词在语料库中的出现频率
二元模型的信息熵计算公式为: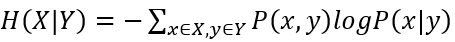
其中联合概率P(x,y)可近似等于每个二元词组在语料库中出现的频率,条件概率P(x|y)可近似等于每个二元词组在语料库中出现的频率与以该二元词组的第一个词为词首的二元词组的频数的比值。
三元模型的信息熵计算公式为: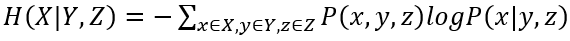
其中联合概率P(x,y,z)可近似等于每个三元词组在语料库中出现的频率,条件概率P(x|y,z)可近似等于每个三元词组在语料库中出现的频率与以该三元词组的前两个词为词首的三元词组的频数的比值。
三、 实验内容
1、中文语料的预处理
数据库中的语料是txt格式的,其中包含得有部分代码和无用的符号,首先需要对数据进行一下预处理,其中包括删除隐藏符号(如换行符、分页符等);.删除爬虫得到的无关信息与字符;删除文中的标点符号,因为标点符号对于中文语料库的信息并无意义。
代码如下(中文语料的预处理):
import os
import re
from collections import Counter
def DFS_file_search(dict_name):
# list.pop() list.append()这两个方法就可以实现栈维护功能
stack = []
result_txt = []
stack.append(dict_name)
while len(stack) != 0: # 栈空代表所有目录均已完成访问
temp_name = stack.pop()
try:
temp_name2 = os.listdir(temp_name) # list ["","",...]
for eve in temp_name2:
stack.append(temp_name + "\\" + eve) # 维持绝对路径的表达
except NotADirectoryError:
result_txt.append(temp_name)
return result_txt
path_list = DFS_file_search(r".\jyxstxtqj_downcc.com")
# path_list 为包含所有小说文件的路径列表
corpus = []
for path in path_list:
with open(path, "r", encoding="ANSI") as file:
text = [line.strip("\n").replace("\u3000", "").replace("\t", "") for line in file][3:]
corpus += text
# corpus 存储语料库,其中以每一个自然段为一个分割
regex_str = ".*?([^\u4E00-\u9FA5]).*?"
english = u'[a-zA-Z0-9’!"#$%&\'()*+,-./::;「<=>?@,。?★、…【】《》?“”‘’![\\]^_`{|}~]+'
symbol = []
for j in range(len(corpus)):
corpus[j] = re.sub(english, "", corpus[j])
symbol += re.findall(regex_str, corpus[j])
count_ = Counter(symbol)
count_symbol = count_.most_common()
noise_symbol = []
for eve_tuple in count_symbol:
if eve_tuple[1] < 200:
noise_symbol.append(eve_tuple[0])
noise_number = 0
for line in corpus:
for noise in noise_symbol:
line.replace(noise, "")
noise_number += 1
print("完成的噪声数据替换点:", noise_number)
print("替换的噪声符号:")
for i in range(len(noise_symbol)):
print(noise_symbol[i], end=" ")
if i % 50 == 0:
print()
with open("预处理后的文本1.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in corpus:
if len(line) > 1:
print(line, file=f)
2、计算N-Gram模型下的中文的平均信息熵
本文的统计语言模型是基于词的,因此需要对中文句子进行分词,选用jieba分词系统——python中文分词系统对句子进行分词。其中包括jieba.cut——给定中文字符串,分解后返回一个迭代器,需要用for循环访问;jieba.cut_for_search——该方法和cut一样,分解后返回一个迭代器,需要用for循环访问。不过它是搜索引擎模式,在精确模式的基础上,对长词再次切分,提高召回率,适合用于搜索引擎分词;jieba.lcut——和jieba.cut使用方法一样,不过返回的是列表。
由于一元模型不需要考虑上下文关系,所以其读取语料的方式与二元模型和三元模型不一样。
代码如下(1-Gram):
import jieba
from collections import Counter
import math
with open("预处理后的文本.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
corpus = [eve.strip("\n") for eve in f]
# 1-gram
token = []
for para in corpus:
token += jieba.lcut(para)
token_num = len(token)
ct = Counter(token)
vocab1 = ct.most_common()
entropy_1gram = sum([-(eve[1]/token_num)*math.log((eve[1]/token_num),2) for eve in vocab1])
print("词库总词数:", token_num, " ", "不同词的个数:", len(vocab1))
print("出现频率前10的1-gram词语:", vocab1[:10])
print("entropy_1gram:", entropy_1gram)
二元模型和三元模型需要考虑上下文关系,因此使用条件熵计算。不能直接去掉所有标点符号得到无分隔的语料。
代码如下(2-Gram):
import jieba
from collections import Counter
import math
import re
def remove_punctuation(line):
rule = re.compile(r"[^a-zA-Z0-9\u4e00-\u9fa5]")
line = rule.sub('',line)
return line
def is_contain_chinese(check_str):
"""
判断字符串中是否包含中文
:param check_str: {str} 需要检测的字符串
:return: {bool} 包含返回True, 不包含返回False
"""
for ch in check_str:
if u'\u4e00' <= ch <= u'\u9fff':
return True
return False
with open("预处理后的文本1.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
corpus = [eve.strip("\n") for eve in f]
# 2-gram
def combine2gram(cutword_list):
if len(cutword_list) == 1:
return []
res = []
for i in range(len(cutword_list)-1):
res.append(cutword_list[i] + " " + cutword_list[i+1])
return res
token_2gram = []
for para in corpus:
cutword_list = jieba.lcut(para)
token_2gram += combine2gram(cutword_list)
# print(token_2gram)
# 2-gram的频率统计
token_2gram_num = len(token_2gram)
ct2 = Counter(token_2gram)
vocab2 = ct2.most_common()
# print(vocab2[:20])
# 2-gram相同句首的频率统计
same_1st_word = [eve.split(" ")[0] for eve in token_2gram]
assert token_2gram_num == len(same_1st_word)
ct_1st = Counter(same_1st_word)
vocab_1st = dict(ct_1st.most_common())
entropy_2gram = 0
for eve in vocab2:
p_xy = eve[1]/token_2gram_num
first_word = eve[0].split(" ")[0]
# p_y = eve[1]/vocab_1st[first_word]
entropy_2gram += -p_xy*math.log(eve[1]/vocab_1st[first_word], 2)
L = [[0]*2 for i in range(10)]
i = 0
j = 1
while True:
L[i][0] = vocab2[j][0]
L[i][1] = vocab2[j][1]
L[i][0] = L[i][0].replace(' ', '')
L[i][0] = remove_punctuation(L[i][0])
if not is_contain_chinese(L[i][0]):
j = j+1
continue
i = i+1
j = j+1
if i == 10:
break
print("词库总词数:", token_2gram_num, " ", "不同词的个数:", len(vocab2))
print("出现频率前10的2-gram词语:", L)
print("entropy_2gram:", entropy_2gram)
代码如下(3-Gram):
import jieba
from collections import Counter
import math
import re
def remove_punctuation(line):
rule = re.compile(r"[^a-zA-Z0-9\u4e00-\u9fa5]")
line = rule.sub('',line)
return line
def is_contain_chinese(check_str):
"""
判断字符串中是否包含中文
:param check_str: {str} 需要检测的字符串
:return: {bool} 包含返回True, 不包含返回False
"""
for ch in check_str:
if u'\u4e00' <= ch <= u'\u9fff':
return True
return False
with open("预处理后的文本.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
corpus = [eve.strip("\n") for eve in f]
# 3-gram
def combine3gram(cutword_list):
if len(cutword_list) <= 2:
return []
res = []
for i in range(len(cutword_list)-2):
res.append(cutword_list[i] + cutword_list[i+1] + " " + cutword_list[i+2] )
return res
token_3gram = []
for para in corpus:
cutword_list = jieba.lcut(para)
# cutword_list = [removePunctuation(eve) for eve in cutword_list if removePunctuation(eve) != ""]
token_3gram += combine3gram(cutword_list)
# 3-gram的频率统计
token_3gram_num = len(token_3gram)
ct3 = Counter(token_3gram)
vocab3 = ct3.most_common()
# print(vocab3[:20])
# 3-gram相同句首两个词语的频率统计
same_2st_word = [eve.split(" ")[0] for eve in token_3gram]
assert token_3gram_num == len(same_2st_word)
ct_2st = Counter(same_2st_word)
vocab_2st = dict(ct_2st.most_common())
entropy_3gram = 0
for eve in vocab3:
p_xyz = eve[1]/token_3gram_num
first_2word = eve[0].split(" ")[0]
entropy_3gram += -p_xyz*math.log(eve[1]/vocab_2st[first_2word], 2)
L = [[0]*2 for i in range(10)]
i = 0
j = 1
while True:
L[i][0] = vocab3[j][0]
L[i][1] = vocab3[j][1]
L[i][0] = L[i][0].replace(' ', '')
L[i][0] = remove_punctuation(L[i][0])
if not is_contain_chinese(L[i][0]):
j = j+1
continue
i = i+1
j = j+1
if i == 10:
break
print("词库总词数:", token_3gram_num, " ", "不同词的个数:", len(vocab3))
print("出现频率前10的3-gram词语:", L)
print("entropy_3gram:", entropy_3gram)
四、实验结果
1、一元模型
词库总词数:4314429
不同词的个数:173005
信息熵:12.166792988733498
出现频率前10的一元词语:“的”——115604、“了”——104527、“他”——64712、“是”——64457、“道”——58623、“我”——57483、“你”——56679、“在”——43691、“也”——32606、“这”——32199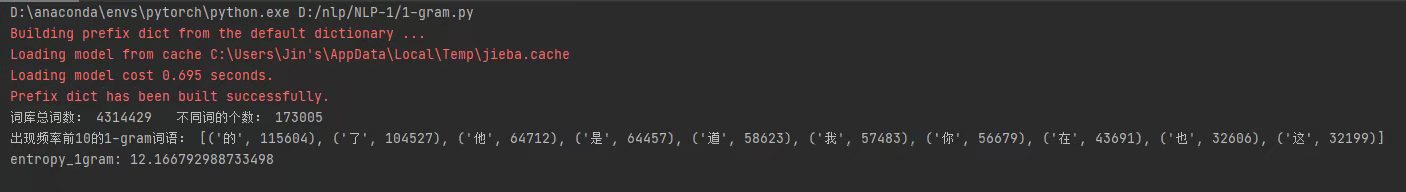
2、二元模型
词库总词数:4255111
不同词的个数:1950585
信息熵:6.94497412025617
出现频率前10的二元词语:
“叫道”——5009、“道我”——4953、“笑道”——4953、“听得”——4202、“都是”——3905、“了他”——3638、“他的”——3497、“也是”——3201、“的一声”——3102、“只听”——2970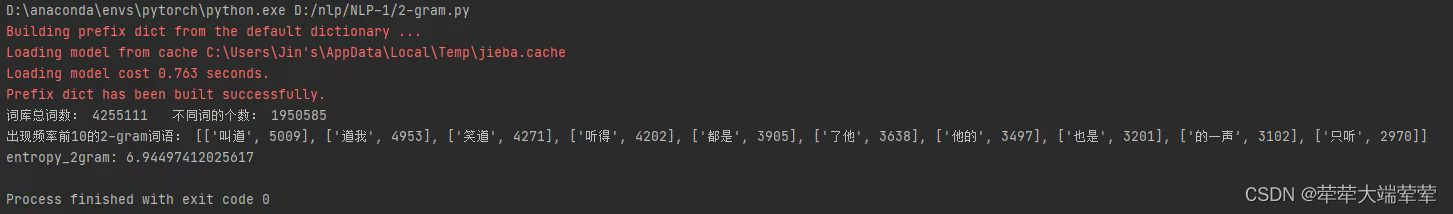
3、三元模型
词库总词数:4196042
不同词的个数:3482119
信息熵:2.3506888268504076
出现频率前10的三元词语:
“忽听得”——1137、“站起身来”——733、“哼了一声”——573、“笑道你”——566、“吃了一惊”——534、“点了点头”——503、“啊的一声”——481、“说到这里”——477、“了他的”——454、“跟你说”——441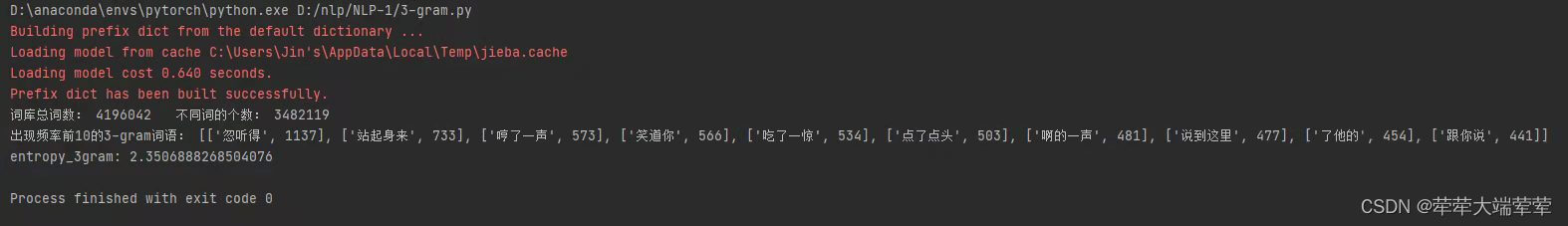
4、实验结果分析
对比1-Gram、2-Gram、3-Gram三种语言模型得到的结果可以看出,N值越大即考虑前后文关系的长度越大,不同词出现的个数也就越多。考虑原因为长度的增加,也增加了由字组合成词的组合个数,所以会出现更多不同的词。
此外,由三者对比可知,随着N取值变大,文本的信息熵则越小。考虑原因为当N取值越大,通过分词后得到的文本中词组的分布越简单,通过分析,可知当N越大时,其能组成的固定的词的数量越少,固定的词能减少由字或短词打乱文章的机会,因此,文章变得更加有序,由字组成词和组成句的不确定性减少,进而文本的信息熵降低。
总结
本文借鉴了前人的工作
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50891266/article/details/115723958?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522164863247216780255276249%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fall.%2522%257D&request_id=164863247216780255276249&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2allfirst_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-1-115723958.142v5pc_search_result_cache,143v6register&utm_term=Entropy+of+English&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
但在实验过程中,发现前人工作中存在着分词时,将分段字符< s >也当做为一个词语或的问题存在,在代码中修复了这个问题。
相关代码可见NLP-1
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容







所有评论(0)