NLP实战之HAN文本分类
HAN(层叠注意力)神经网络文本分类原理讲解HAN出处:论文Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification可以参见讲解文献阅读笔记:Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification这篇论文表示,对文档/较长文本进行分类的时候,仅仅对word粒度进行Atten
HAN(层叠注意力)神经网络文本分类
原理讲解
HAN出处:论文Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification
可以参见讲解文献阅读笔记:Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification
这篇论文表示,对文档/较长文本进行分类的时候,仅仅对word粒度进行Attention是不够的,还需要对各个句子(短句)进行Attention的学习,不同句子也需要分配不同的权重,每个句子里的词语也分配不同的权重。
网络结构
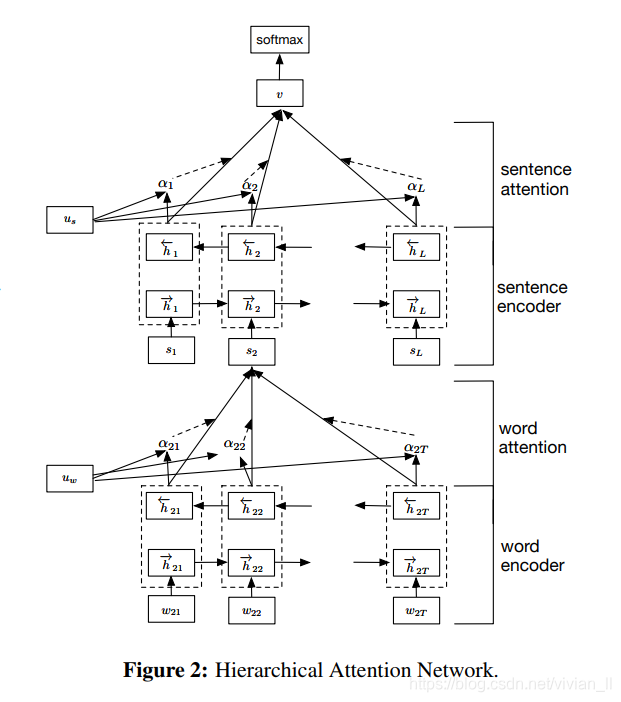
- Word Encoder. 对词汇进行编码,建立词向量。接着用双向 RNN 从单词的两个方向汇总信息来获取单词的注释,因此将上下文信息合并到句子向量中。
- Word Attention. 对每句话的词语进行Attention操作,最后每句话都有一个特征向量,可以看做句向量
- Sentence Encoder. 与word encoder相似,对句子级别也使用双向 RNN 获取上下句的信息
- Sentence Attention. 与 word Attention相似,对所有句子进行Attention操作,获得一个每个句子加权平均作为整个输入的特征向量
- Document Classification. 常规的输出分类结果
本文实现
此处的 Attention 的实现使用了 FeedForwardAttention 的实现方式,与 TextAttBiRNN 中的 Attention 相同。
HAN 的网络结构: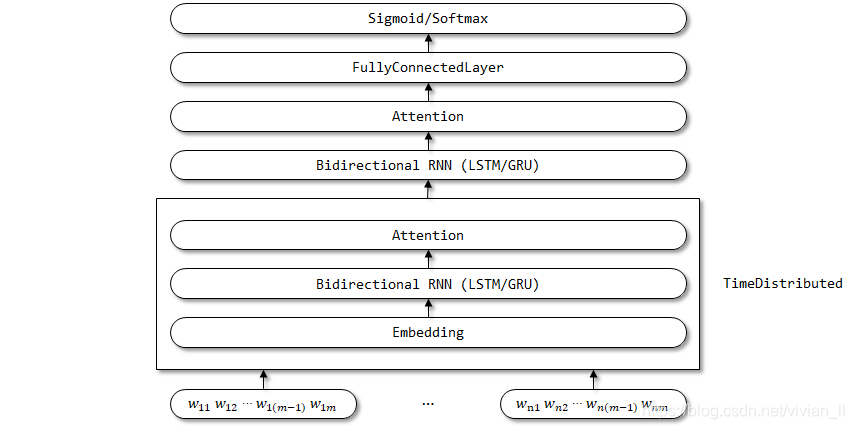
此处使用了 TimeDistributed 包装器,希望 Embedding、Bidirectional RNN 和 Attention 层的参数能够在时间步维度上共享。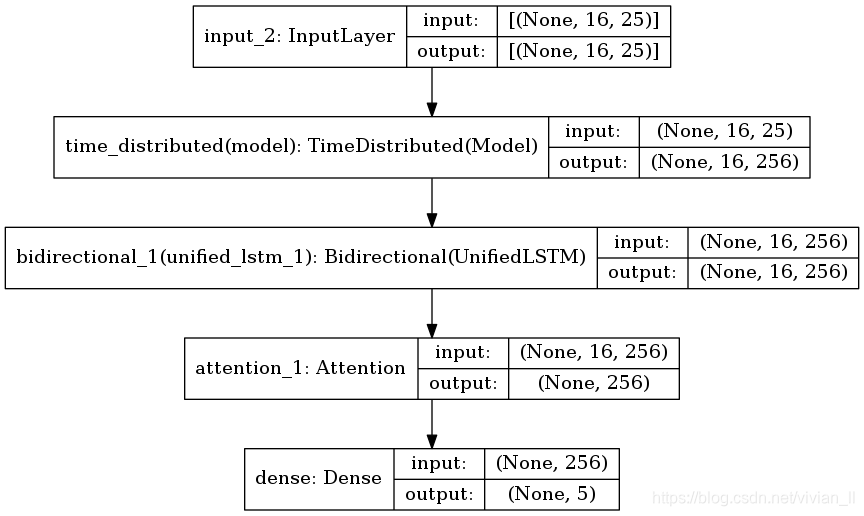
输入层
与其他的文本分类模型的输入不同,在这里输入层变成了句子数量×每句词语数量,在代码中对数据处理比较粗暴,直接将原来的一句话padding补全到句子数量×词语数量的长度,然后reshape到所需的维度。因此这里每个样本内容其实还是原来的一句话,所以在这个训练数据中,可以理解为进行了层次化的Attention。
word粒度Attention层
word粒度的操作,使用了keras中TimeDistributed层进行了封装,它的原理是将这个层中的操作对输入的最后一维进行使用,在这里就是该层中的Attention操作是对输入的最后一维,也就是词语这一维进行使用。举个例子,我们的数据输入是(32, 10, 16)维度,我们在TimeDistributed层中添加了一个Dense(16, 8)的全连接层,那么经过该TimeDistributed层的输出就是(32, 10, 8)维度。
Attention的代码与上一次Bi-LSTM+Attention代码一样,因此输出变成了16(句子数)×256(每句句子256维)
sentence粒度Attention层
这一层操作还是与word粒度Attention相同,对每句话进行了Attention的加权求和,得到这16句话最终加权的结果,也是256维。
输出层
依旧是接5分类的全连接层进行输出。
定义网络结构
首先定义Attention类,和上一篇博文text-attition-BiRNN中的定义一样。
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
#from tensorflow.python.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras import initializers, regularizers, constraints
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer
#from keras.engine.topology import Layer
class Attention(Layer):
def __init__(self, step_dim,
W_regularizer=None, b_regularizer=None,
W_constraint=None, b_constraint=None,
bias=True, **kwargs):
"""
Keras Layer that implements an Attention mechanism for temporal data.
Supports Masking.
Follows the work of Raffel et al. [https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.08756]
# Input shape
3D tensor with shape: `(samples, steps, features)`.
# Output shape
2D tensor with shape: `(samples, features)`.
:param kwargs:
Just put it on top of an RNN Layer (GRU/LSTM/SimpleRNN) with return_sequences=True.
The dimensions are inferred based on the output shape of the RNN.
Example:
# 1
model.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True))
model.add(Attention())
# next add a Dense layer (for classification/regression) or whatever...
# 2
hidden = LSTM(64, return_sequences=True)(words)
sentence = Attention()(hidden)
# next add a Dense layer (for classification/regression) or whatever...
"""
self.supports_masking = True
self.init = initializers.get('glorot_uniform')
self.W_regularizer = regularizers.get(W_regularizer)
self.b_regularizer = regularizers.get(b_regularizer)
self.W_constraint = constraints.get(W_constraint)
self.b_constraint = constraints.get(b_constraint)
self.bias = bias
self.step_dim = step_dim
self.features_dim = 0
super(Attention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
assert len(input_shape) == 3
self.W = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[-1],),
initializer=self.init,
name='{}_W'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.W_regularizer,
constraint=self.W_constraint)
self.features_dim = input_shape[-1]
if self.bias:
self.b = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[1],),
initializer='zero',
name='{}_b'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.b_regularizer,
constraint=self.b_constraint)
else:
self.b = None
self.built = True
def compute_mask(self, input, input_mask=None):
# do not pass the mask to the next layers
return None
def call(self, x, mask=None):
features_dim = self.features_dim
step_dim = self.step_dim
e = K.reshape(K.dot(K.reshape(x, (-1, features_dim)), K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1))), (-1, step_dim)) # e = K.dot(x, self.W)
if self.bias:
e += self.b
e = K.tanh(e)
a = K.exp(e)
# apply mask after the exp. will be re-normalized next
if mask is not None:
# cast the mask to floatX to avoid float64 upcasting in theano
a *= K.cast(mask, K.floatx())
# in some cases especially in the early stages of training the sum may be almost zero
# and this results in NaN's. A workaround is to add a very small positive number ε to the sum.
a /= K.cast(K.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True) + K.epsilon(), K.floatx())
a = K.expand_dims(a)
c = K.sum(a * x, axis=1)
return c
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0], self.features_dim
然后定义HAN类。
注意这里的word级的attention和sentence级的attention不同,句子级的需要用TimeDistributed。
from tensorflow.keras import Input, Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Dense, Dropout, Bidirectional, LSTM, TimeDistributed
class HAN(object):
def __init__(self, maxlen_sentence, maxlen_word, max_features, embedding_dims,
class_num=5,
last_activation='softmax'):
self.maxlen_sentence = maxlen_sentence
self.maxlen_word = maxlen_word
self.max_features = max_features
self.embedding_dims = embedding_dims
self.class_num = class_num
self.last_activation = last_activation
def get_model(self):
# Word part
input_word = Input(shape=(self.maxlen_word,))
x_word = Embedding(self.max_features, self.embedding_dims, input_length=self.maxlen_word)(input_word)
x_word = Bidirectional(LSTM(128, return_sequences=True))(x_word) # LSTM or GRU
x_word = Attention(self.maxlen_word)(x_word)
model_word = Model(input_word, x_word)
# Sentence part
input = Input(shape=(self.maxlen_sentence, self.maxlen_word))
x_sentence = TimeDistributed(model_word)(input)
x_sentence = Bidirectional(LSTM(128, return_sequences=True))(x_sentence) # LSTM or GRU
x_sentence = Attention(self.maxlen_sentence)(x_sentence)
output = Dense(self.class_num, activation=self.last_activation)(x_sentence)
model = Model(inputs=input, outputs=output)
return model
数据处理与训练
和之前的模型类似
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import sequence
import random
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import sys
sys.path.append('../data/lesson2_data')
from utils import *
# 路径等配置
data_dir = "../data/lesson2_data/data"
vocab_file = "../data/lesson2_data/vocab/vocab.txt"
vocab_size = 40000
# 神经网络配置
max_features = 40001
maxlen_sentence = 16
maxlen_word = 25
batch_size = 64
embedding_dims = 50
epochs = 10
print('数据预处理与加载数据...')
# 如果不存在词汇表,重建
if not os.path.exists(vocab_file):
build_vocab(data_dir, vocab_file, vocab_size)
# 获得 词汇/类别 与id映射字典
categories, cat_to_id = read_category()
words, word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_file)
# 全部数据
x, y = read_files(data_dir)
data = list(zip(x,y))
del x,y
# 乱序
random.shuffle(data)
# 切分训练集和测试集
train_data, test_data = train_test_split(data)
# 对文本的词id和类别id进行编码
x_train = encode_sentences([content[0] for content in train_data], word_to_id)
y_train = to_categorical(encode_cate([content[1] for content in train_data], cat_to_id))
x_test = encode_sentences([content[0] for content in test_data], word_to_id)
y_test = to_categorical(encode_cate([content[1] for content in test_data], cat_to_id))
print('对序列做padding')
x_train = sequence.pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=maxlen_sentence * maxlen_word)
x_test = sequence.pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen=maxlen_sentence * maxlen_word)
x_train = x_train.reshape((len(x_train), maxlen_sentence, maxlen_word))
x_test = x_test.reshape((len(x_test), maxlen_sentence, maxlen_word))
print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape)
print('x_test shape:', x_test.shape)
print('构建模型...')
model = HAN(maxlen_sentence, maxlen_word, max_features, embedding_dims).get_model()
model.compile('adam', 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
print('Train...')
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=2, mode='max')
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=[early_stopping],
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
print('Test...')
result = model.predict(x_test)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容








所有评论(0)