CRNN不定长验证码识别
blank为0使得我们在计算CTCLoss之前需要对样本进行移位,例如a、b、c对应的标签为0、1、2,我们需要把相应的标签改为1、2、3,才能计算CTCLoss。而在进行推理的过程中,则需要把预测的结果的index进行减一,映射回原始正确的标签。关于验证码识别的任务,我们可以通过使用卷积神经网络采用多标签分类的方法来完成,但是当验证码是不定长的时候,就无法使用多标签分类的方法来解决了,在这类任务
原文:CRNN不定长验证码识别 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
一、不定长验证码识别
关于验证码识别的任务,我们可以通过使用卷积神经网络采用多标签分类的方法来完成,但是当验证码是不定长的时候,就无法使用多标签分类的方法来解决了,在这类任务中,识别的目标是类似于序列的长条形图片,我们将会使用自然语言处理以及时间序列预测任务中的循环神经网络算法。本节将通过CRNN算法来完成不定长验证码的识别。不同于一般的时间序列预测,CRNN中的循环神经网络取整个输出序列作为结果,而非最后一个输出值。

定长验证码
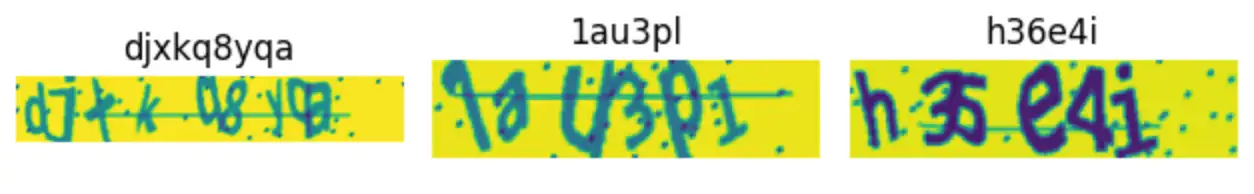
不定长验证码
二、CRNN模型介绍
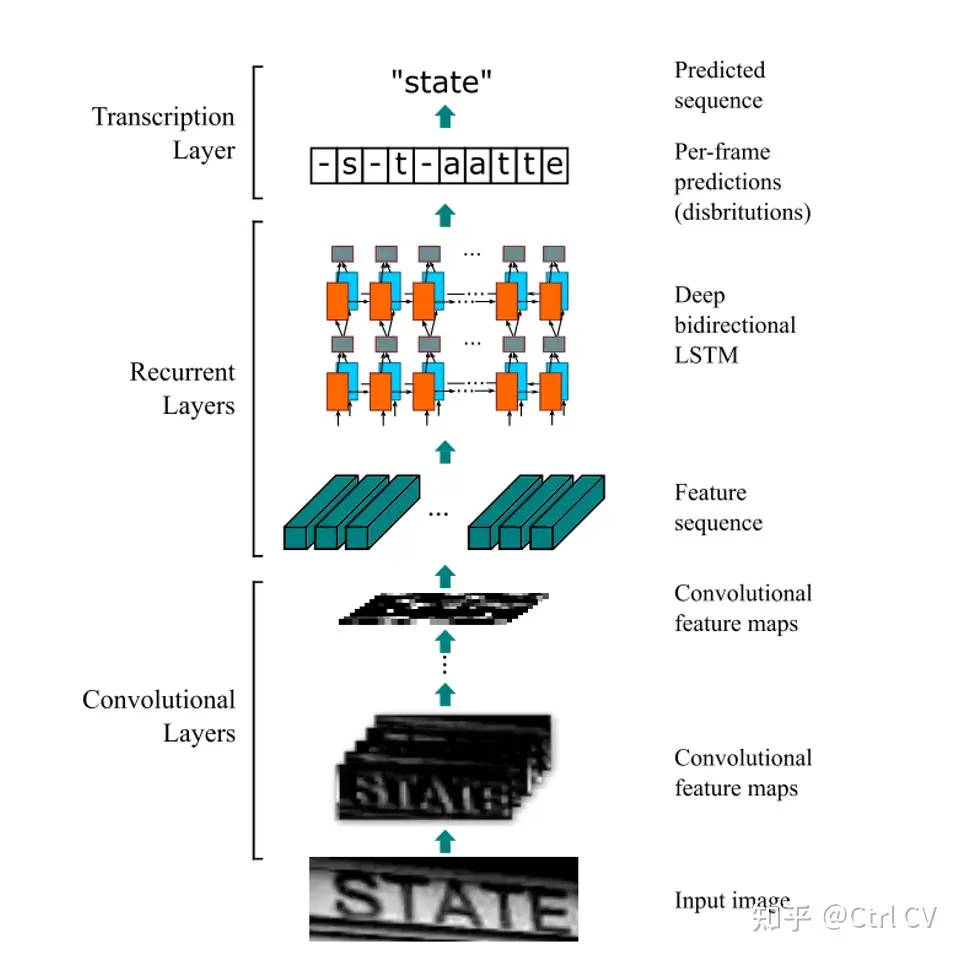
CRNN算法的训练流程如下:
(1)输入包含文本的图片,首先经过卷积层计算之后得到序列特征
(2)将序列特征输入RNN模型进行计算,得到输出序列
(3)计算输出序列与图片标签之间的CTCLoss,进行反向传播,更新参数
CRNN算法的测试流程需要经过解码器处理才能得到识别的结果,相邻结果如果是同一个字符则合并,如果是空格则略过。
三、CRNN模型结构
CNN部分是由conv+bn+relu组合搭建的序列网络。
RNN部分采用双层双向LSTM / GRU拼接而成。
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class BidirectGRU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(BidirectGRU, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_size, bidirectional=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size*2, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
r, _ = self.rnn(x)
t, b, h = r.size()
x = r.view(t*b, h)
out = self.fc(x)
return out.view(t, b, -1)
class R(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(R, self).__init__(
BidirectGRU(input_size, hidden_size, hidden_size),
BidirectGRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, output_size)
)
class ConvBNRelu(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, bn=False):
# super(ConvBNRelu, self).__init__()
if bn:
super(ConvBNRelu, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
else:
super(ConvBNRelu, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
class C(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, height, in_channels):
super(C, self).__init__()
cs = [1, 64, 128, 256, 256, 512, 512, 512]
ps = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
ks = [3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2]
cnn = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(7):
if i in [0, 1, 2, 3, 6]:
cnn.add_module('conv{}'.format(i),
ConvBNRelu(cs[i], cs[i+1], ks[i], 1, ps[i]))
if i in [4, 5]:
cnn.add_module('conv{}'.format(i),
ConvBNRelu(cs[i], cs[i+1], ks[i], 1, ps[i], bn=True))
if i in [0, 1]:
cnn.add_module('pool{}'.format(i), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
if i in [3, 5]:
cnn.add_module('pool{}'.format(i), nn.MaxPool2d(2, (2, 1), (0, 1)))
self.cnn = cnn
def forward(self, x):
return self.cnn(x)
class CRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, height, in_channels, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(CRNN, self).__init__()
self.cnn = C(height, in_channels)
self.rnn = R(input_size, hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
conv = self.cnn(x)
conv = conv.squeeze(2)
conv = conv.permute(2, 0, 1)
output = self.rnn(conv)
return F.log_softmax(output, dim=2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import torch
net = CRNN(32, 1, 512, 256, 256)
print(net)
x = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 100)
out = net(x)
print(out.shape)四、模型训练
关于解码,一般的分类模型在进行解码时,只需要使用torch.argmax求出最大值的index即可,而在CRNN中,输出序列中有很多的blank和重复值都需要进行删除。blank为0使得我们在计算CTCLoss之前需要对样本进行移位,例如a、b、c对应的标签为0、1、2,我们需要把相应的标签改为1、2、3,才能计算CTCLoss。而在进行推理的过程中,则需要把预测的结果的index进行减一,映射回原始正确的标签。
from model import CRNN
from data import train_dl, test_dl, char_list
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
from tqdm import tqdm
from config import device, ckpt
import os.path as osp
net = CRNN(32, 1, 512, 256, len(char_list)+1)
class strLabelConverter(object):
def __init__(self, alphabet):
self.alphabet = alphabet + 'c'
def encode(self, labels):
length = []
result = []
for label in labels:
length.append(len(label))
for index in label:
result.append(index.item())
text = result
return torch.IntTensor(text), torch.IntTensor(length)
def decode(self, t, length):
char_list = []
for i in range(length):
if t[i] != 0 and (not (i > 0 and t[i-1] == t[i])):
char_list.append(self.alphabet[t[i] - 1])
return ''.join(char_list)
converter = strLabelConverter(''.join(char_list))
def train():
net.to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
criteron = nn.CTCLoss(reduction='sum')
if osp.exists(ckpt):
c = torch.load(ckpt)
net.load_state_dict(c['state_dict'])
best_loss = c['best_loss']
else:
best_loss = 1e9
for m in range(100):
epoch_loss = 0.0
for n, (image, label) in tqdm(enumerate(train_dl), total=len(train_dl)):
optimizer.zero_grad()
image = image.to(device)
out = net(image)
text, lengths = converter.encode(label)
pred_lengths = torch.IntTensor([out.size(0)] * out.shape[1])
loss = criteron(out, text, pred_lengths, lengths)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_loss /= len(train_dl.dataset)
print('epoch{}_loss'.format(m), epoch_loss)
val_loss = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
for m, (image, label) in tqdm(enumerate(test_dl), total=len(test_dl)):
image = image.to(device)
out = net(image)
text, lengths = converter.encode(label)
pred_lengths = torch.IntTensor([out.size(0)] * out.shape[1])
loss = criteron(out, text, pred_lengths, lengths)
val_loss += loss.item()
val_loss /= len(test_dl.dataset)
print('val{}_loss'.format(m), val_loss)
if val_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss
torch.save(
{
'state_dict': net.state_dict(),
'best_loss': best_loss
},
ckpt
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()五、模型测试
训练完成之后加载模型进行预测:
from torchvision import transforms
import torch
import numpy as np
from data import test_dl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from config import device, ckpt, char_list
from train import converter, net
if __name__ == '__main__':
params = torch.load(ckpt)
net.load_state_dict(params['state_dict'])
print('current loss: {}'.format(params['best_loss']))
net.to(device)
col = 0
row = 1
for d in test_dl.dataset:
img = d[0].convert('L')
h, w = img.size
img = img.resize((int(h*(32/w)), 32))
img_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()(img).unsqueeze(0)
label = d[1].int()
label = [char_list[i - 1] for i in label]
preds = net(img_tensor.to(device))
_, preds = preds.max(2)
preds = preds.transpose(1, 0).contiguous().view(-1)
pred_size = torch.IntTensor([preds.size(0)])
sim_pred = converter.decode(preds.data, pred_size.data)
plt.subplot(330+col+1)
plt.title(''.join(sim_pred))
plt.imshow(np.array(img))
plt.axis('off')
col += 1
if col == 9:
break
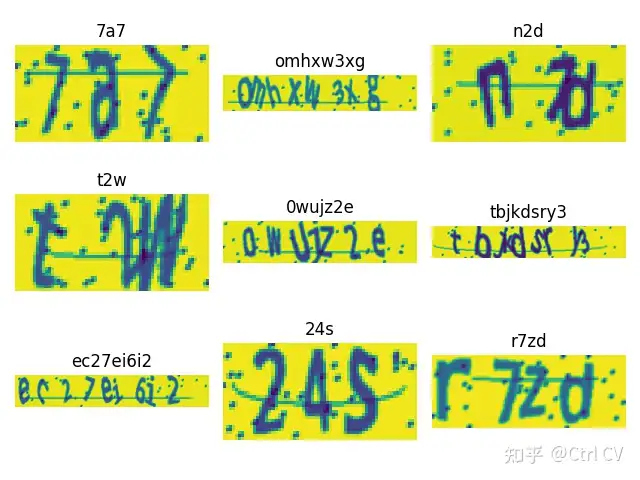
plt.show()结果如下,可以看到验证码预测的结果都是正确的:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献26条内容
已为社区贡献26条内容









所有评论(0)