【人工智能】构建基于 Qwen1.5-7B-Chat 的轻量级 Python 对话助手
Qwen 系列语言模型提供了功能强大且开源的大型语言模型,可用于各种自然语言处理任务。本文将展示如何在 Python 中设置并运行一个由 Qwen 模型驱动的个人助理应用程序——具体使用 Qwen1.5-7B-Chat 模型。该模型是一个高效且相对轻量的 70 亿参数对话模型,专为会话场景优化。文中示例代码可直接在 Google Colab 等 Python 笔记本中运行,也可轻松适配在本地环境使
【精选优质专栏推荐】
- 《AI 技术前沿》 —— 紧跟 AI 最新趋势与应用
- 《网络安全新手快速入门(附漏洞挖掘案例)》 —— 零基础安全入门必看
- 《BurpSuite 入门教程(附实战图文)》 —— 渗透测试必备工具详解
- 《网安渗透工具使用教程(全)》 —— 一站式工具手册
- 《CTF 新手入门实战教程》 —— 从题目讲解到实战技巧
- 《前后端项目开发(新手必知必会)》 —— 实战驱动快速上手
每个专栏均配有案例与图文讲解,循序渐进,适合新手与进阶学习者,欢迎订阅。

前言
Qwen 系列语言模型提供了功能强大且开源的大型语言模型,可用于各种自然语言处理任务。
本文将展示如何在 Python 中设置并运行一个由 Qwen 模型驱动的个人助理应用程序——具体使用 Qwen1.5-7B-Chat 模型。该模型是一个高效且相对轻量的 70 亿参数对话模型,专为会话场景优化。文中示例代码可直接在 Google Colab 等 Python 笔记本中运行,也可轻松适配在本地环境使用。
实践教程
由于创建一个由 Qwen 驱动的助手需要安装多个依赖库,我们首先安装这些库并验证其版本,以尽可能保证与已安装版本的兼容性。
pip install -q transformers accelerate bitsandbytes einops ipywidgets
在可用的情况下,我们还会设置 GPU,以加快模型推理速度。模型在首次调用时会进行初始化。
以下代码展示了这些初始设置步骤:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import time
from IPython.display import display, HTML, clear_output
import ipywidgets as widgets
import sys
import os
# 验证已安装的软件包和依赖项
try:
import bitsandbytes as bnb
print("Successfully imported bitsandbytes")
except ImportError:
print("Error importing bitsandbytes. Attempting to install again...")
!pip install -q bitsandbytes --upgrade
import bitsandbytes as bnb
# 安装所需软件包(如果已经安装,可以注释掉下面这行)
!pip install -q transformers accelerate bitsandbytes einops
# 设置设备,优先使用 GPU(如果可用)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
接下来是加载和配置模型。
我们使用 Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat,相较于更大型的模型(如 Qwen2.5-Omni),首次推理速度更快。虽然 Qwen2.5-Omni 性能更强,但不如该系列的轻量版本精简。
像往常一样,加载预训练语言模型时需要一个 tokenizer 将文本输入转换为模型可读取的格式。HuggingFace 的 AutoTokenizer 可以简化这一过程。
为提高效率,我们尝试启用 4-bit 量化,以优化内存使用。
因此代码如下所示:
# 加载 Qwen1.5-7B-Chat 模型 - 公开可用,并且在 Google Colab 的 T4 GPU 上运行效率较高
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat"
print(f"Loading {model_name}...")
start_time = time.time()
# 加载分词器
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
# 尝试使用 4-bit 量化加载模型以提高效率
try:
print("Attempting to load model with 4-bit quantization...")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, # 使用 bfloat16 以获得更好性能
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=True,
quantization_config={"load_in_4bit": True} # 使用 4-bit 量化以优化内存效率
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"4-bit quantization failed with error: {str(e)}")
print("Falling back to 8-bit quantization...")
try:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=True,
load_in_8bit=True # 尝试改用 8-bit 量化
)
except Exception as e2:
print(f"8-bit quantization failed with error: {str(e2)}")
print("Falling back to standard loading (will use more memory)...")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=True
)
load_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Model loaded in {load_time:.2f} seconds")
在构建自定义对话助手时,通常的良好做法是设计一个默认提示词,该提示词会随每次具体请求一起使用,用于调整模型的行为并生成符合需求的回答。以下是一个示例默认提示词:
system_prompt = """You are a helpful, respectful and honest assistant. Always answer as helpfully as possible, while being safe. Your answers should be engaging and fun.
If a question does not make any sense, or is not factually coherent, explain why instead of answering something not correct. If you don't know the answer to a question, please don't share false information."""
接下来定义的函数封装了执行流程中最关键的部分:模型接收用户输入并生成回复。在此,我们将运行一个可连续发出多次请求的对话,因此需要妥善管理聊天历史,并将其作为每次新请求的一部分传入。
def generate_response(user_input, chat_history=None):
if chat_history is None:
chat_history = []
# 格式化对话内容传递给模型
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt}]
# 添加聊天历史,以提供完整上下文
for message in chat_history:
messages.append(message)
# 添加当前用户输入
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
# 分词处理:将消息转换为模型输入格式
prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
# 生成回复:第一次执行可能需要较长时间
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.9,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.pad_token_id or tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
# 解码生成的回复
full_response = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
# 仅提取助手的回复,而不是完整的原始输出
assistant_response = full_response.split(user_input)[-1].strip()
# 如果回复中包含角色标记或其他无关信息,则进一步清理
if "assistant" in assistant_response.lower()[:20]:
assistant_response = assistant_response.split(":", 1)[-1].strip()
return assistant_response
在定义好生成回复的关键函数后,我们可以构建一个简单的用户界面,用于运行并与助手交互。
该界面包含:
-
一个输出显示区域,用于展示对话内容
-
一个输入文本框,用户在其中输入问题
-
两个按钮:一个用于发送请求,一个用于清空聊天
这里使用 widgets 库来实现这些界面元素。
# 为个人助理创建一个简单的用户界面
def create_assistant_ui():
output = widgets.Output()
input_box = widgets.Text(
value='',
placeholder='Ask me anything...', # 占位提示文字
description='Question:', # 输入框标签
layout=widgets.Layout(width='80%')
)
send_button = widgets.Button(description="Send") # 发送按钮
clear_button = widgets.Button(description="Clear Chat") # 清空聊天按钮
chat_history = []
# 处理“发送”按钮点击事件
def on_send_button_clicked(b):
user_input = input_box.value
if not user_input.strip():
return
with output:
print(f"You: {user_input}")
# 显示“正在思考”提示
print("Assistant: Thinking...", end="\r")
# 生成回复
start_time = time.time()
try:
response = generate_response(user_input, chat_history)
end_time = time.time()
# 清除“正在思考”的提示
clear_output(wait=True)
# 显示对话内容
print(f"You: {user_input}")
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
print(f"\n(Response generated in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds)")
# 更新聊天历史
chat_history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
chat_history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
except Exception as e:
clear_output(wait=True)
print(f"You: {user_input}")
print(f"Error generating response: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
# 清空输入框
input_box.value = ''
# 处理“清空聊天”按钮点击事件
def on_clear_button_clicked(b):
with output:
clear_output()
print("Chat cleared!")
chat_history.clear()
# 将按钮点击事件绑定到函数
send_button.on_click(on_send_button_clicked)
clear_button.on_click(on_clear_button_clicked)
# 处理输入框中按下回车键的事件
def on_enter(sender):
on_send_button_clicked(None)
input_box.on_submit(on_enter)
# 布局界面组件
input_row = widgets.HBox([input_box, send_button, clear_button])
ui = widgets.VBox([output, input_row])
return ui
我们还可以设置命令行接口(CLI)来实现聊天工作流:
# 使用模型的更简单方式示例(命令行接口)
def cli_chat():
print("\n=== Starting CLI Chat (type 'exit' to quit) ===")
chat_history = []
while True:
user_input = input("\nYou: ")
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit', 'q']:
print("Goodbye!")
break
print("Assistant: ", end="")
try:
start_time = time.time()
response = generate_response(user_input, chat_history)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"{response}")
print(f"(Generated in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds)")
# 更新聊天历史
chat_history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
chat_history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
接下来是最后两步:
-
定义一个快速测试函数,用于确认模型和依赖项已正确安装并可正常运行。
-
定义一个总控函数,用于启动整个对话助手应用程序,并允许用户选择使用的接口类型(UI 或 CLI)。
# 尝试一个简单的测试查询以确保一切正常
def quick_test():
test_question = "What can you help me with?"
print(f"\nTest Question: {test_question}")
start_time = time.time()
try:
response = generate_response(test_question)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Response: {response}")
print(f"Generation time: {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"Test failed with error: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc() # 打印完整堆栈以便调试
return False
# 应用程序的总控函数:在这里我们可以选择使用哪种界面
def run_assistant():
print("\nRunning quick test...")
test_success = quick_test()
if test_success:
# 询问用户选择哪种界面
interface_choice = input("\nChoose interface (1 for UI, 2 for CLI): ")
if interface_choice == "2":
cli_chat()
else:
print("\nStarting the personal assistant UI...")
assistant_ui = create_assistant_ui()
display(assistant_ui)
# 使用说明
print("\n--- Instructions ---")
print("1. 在文本框中输入你的问题")
print("2. 按回车键或点击 'Send'")
print("3. 等待助手的回复")
print("4. 点击 'Clear Chat' 开始新的对话")
print("----------------------")
else:
print("\n由于测试失败,跳过 UI 启动。")
print("你可以直接调用 cli_chat() 尝试命令行界面")
# 运行对话助手
run_assistant()
试运行
如果一切设置成功,现在就可以与新构建的助手进行互动了。下面是一个对话流程示例片段:
Running quick test...
Test Question: What can you help me with?
Response:
1. General knowledge: I can provide information on a wide range of topics, from history and science to pop culture, current events, and more.
2. Problem-solving: Need help with a math problem, figuring out how to do something, or troubleshooting an issue? I'm here to guide you.
3. Research: If you have a specific topic or question in mind, I can help you find reliable sources and summarize the information for you.
4. Language assistance: Need help with writing, grammar, spelling, or translation? I can assist with that.
5. Fun facts and trivia: Want to impress your friends with interesting facts or just looking for a good laugh? I've got you covered!
6. Time management and organization: Strategies to help you stay on top of your tasks and projects.
7. Personal development: Tips for learning new skills, setting goals, or managing your emotions.
Just let me know what you need, and I'll do my best to assist you! Remember, I can't always give away all the answers, but I'll certainly try to make the process as enjoyable and informative as possible.
Generation time: 18.04 seconds
Choose interface (1 for UI, 2 for CLI):
下面是通过 UI 实时交互的示例:
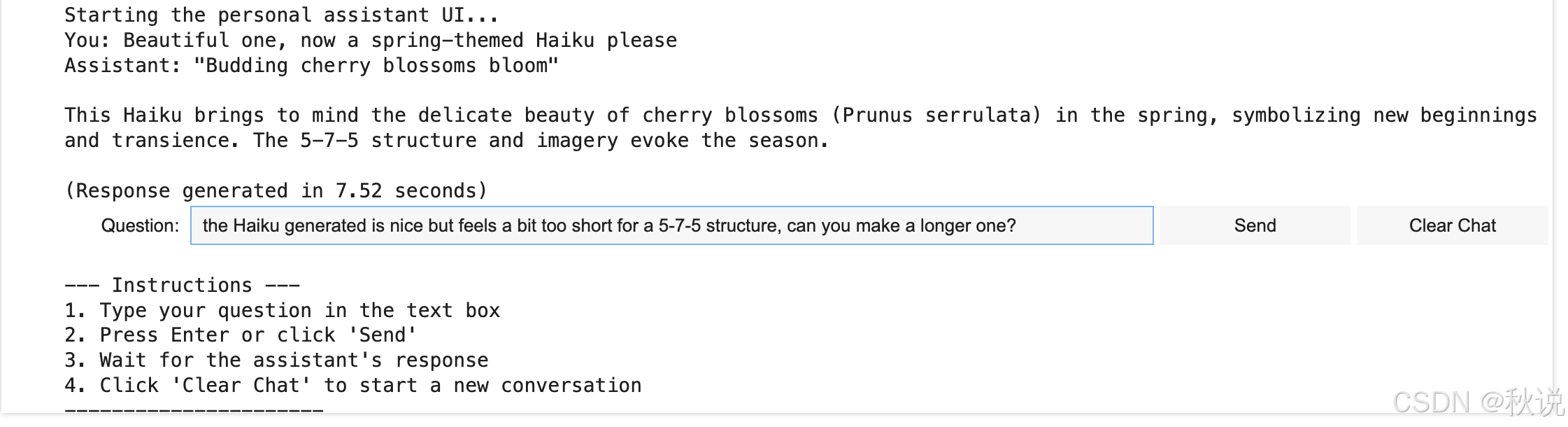
结论
本文演示了如何构建一个由轻量但功能强大的 Qwen 语言模型驱动的简单对话助手应用程序。
该应用程序设计为可在 GPU 环境中高效运行和测试,例如 Google Colab 笔记本提供的环境。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)